How to Configure Bluetooth feature on Omada Controller
Contents
Parameter Optimization Recommendations
Objective
This article details the principle and advantages of Bluetooth IoT technology and provides specific configuration guidelines and application strategies for Bluetooth IoT.
Requirements
- Omada Controller (v5.15.24 and above)
- EAP (Hardware and Firmware all support Bluetooth feature)
- Third-party IoT server
Introduction
With the explosive growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, the high-power consumption and high costs of traditional wireless communication technologies (such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks) have become increasingly prominent. Bluetooth IoT is emerging as a key short-range solution, offering low power use, broad compatibility, flexible networking, and strong security. Common Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocols include Apple's iBeacon protocol, Google's Eddystone protocol, and other proprietary protocols from manufacturers, such as Minew.
Bluetooth IoT is a low-cost indoor positioning solution that can achieve Bluetooth terminal positioning, Bluetooth tag positioning, and Bluetooth data reporting.
The basic principle is that an EAP has built-in Bluetooth that can detect nearby Bluetooth signals. The EAP can roughly estimate the position of a Bluetooth tag based on the signal strength of the Bluetooth frame, and more EAPs can provide more accurate positioning. Multiple EAPs will send the collected Bluetooth signals to the positioning server and application server dedicated to processing the data in order to coordinate tag positioning with other corresponding functions.
The basic principle diagram is as follows:
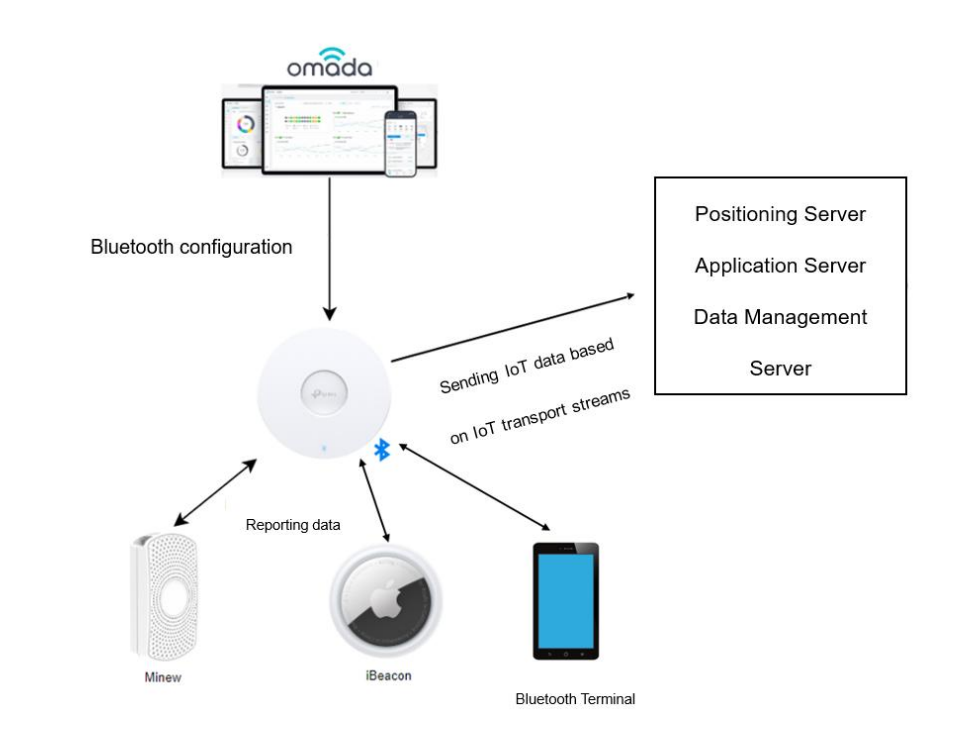
Bluetooth IoT positioning functionality is mainly divided into three parts:
1. The transmission of Bluetooth signals.
2. The collection and reporting of Bluetooth information.
3. The processing of positioning information and its application.
EAPs play an important role in the transmission, collection, and reporting of Bluetooth signals, while the third part mainly relies on third-party servers, with different processing methods used to realize different functions.
Currently, EAPs can actively transmit iBeacon frames, collect Bluetooth information, and report the data to the specified servers to meet different needs.
Configuration
Preparation before Configuration
Step 1. Install and deploy the IoT positioning server. We have not yet officially released our IoT server product. Please prepare a third-party IoT server.
Step 2. Install and deploy BLE tags, securing them to items requiring inventory.
Step 3. Verify that both the EAP hardware and software support Bluetooth.
The configuration includes two parts: Bluetooth advertising and IoT Transport Streams.
The following demonstrates the configuration steps using Omada Network v6.0.0.23 and EAP722 1.0.
The configuration of Bluetooth Advertising
After configuring Bluetooth advertising on an EAP, the EAP will send iBeacon advertising frames with a specific configured UUID-Major-Minor-RSSI Calibration Value field, which can help realize Bluetooth terminal positioning in specific application scenarios.
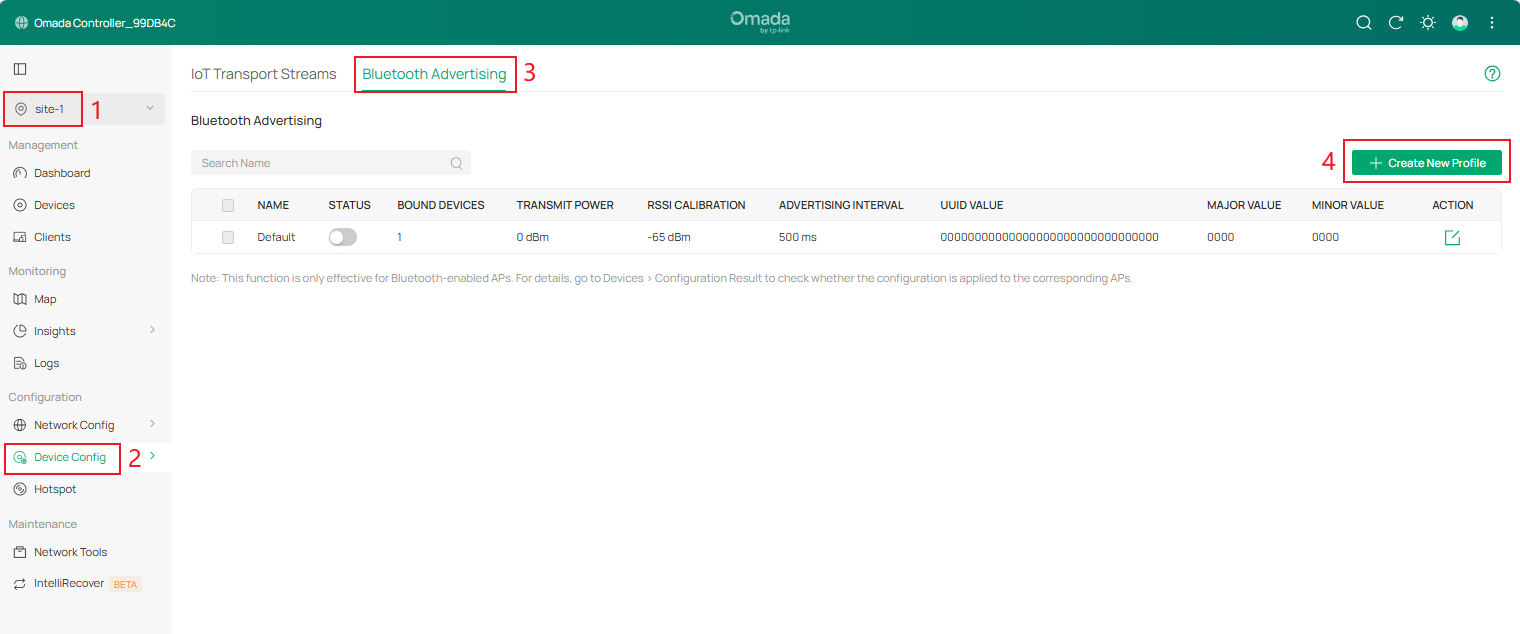
Step 1. Launch the Omada Controller, go to Site View > Device Config > EAP > Bluetooth > Bluetooth Advertising.
On the Bluetooth Advertising page, you can configure rules for the EAP to broadcast iBeacon packets. There is a default profile, which cannot be deleted but can be disabled. You can add an Advertising profile and assign it to the specific EAPs.
Step 2. Click Create New Profile, and configure the iBeacon frame-related parameters.
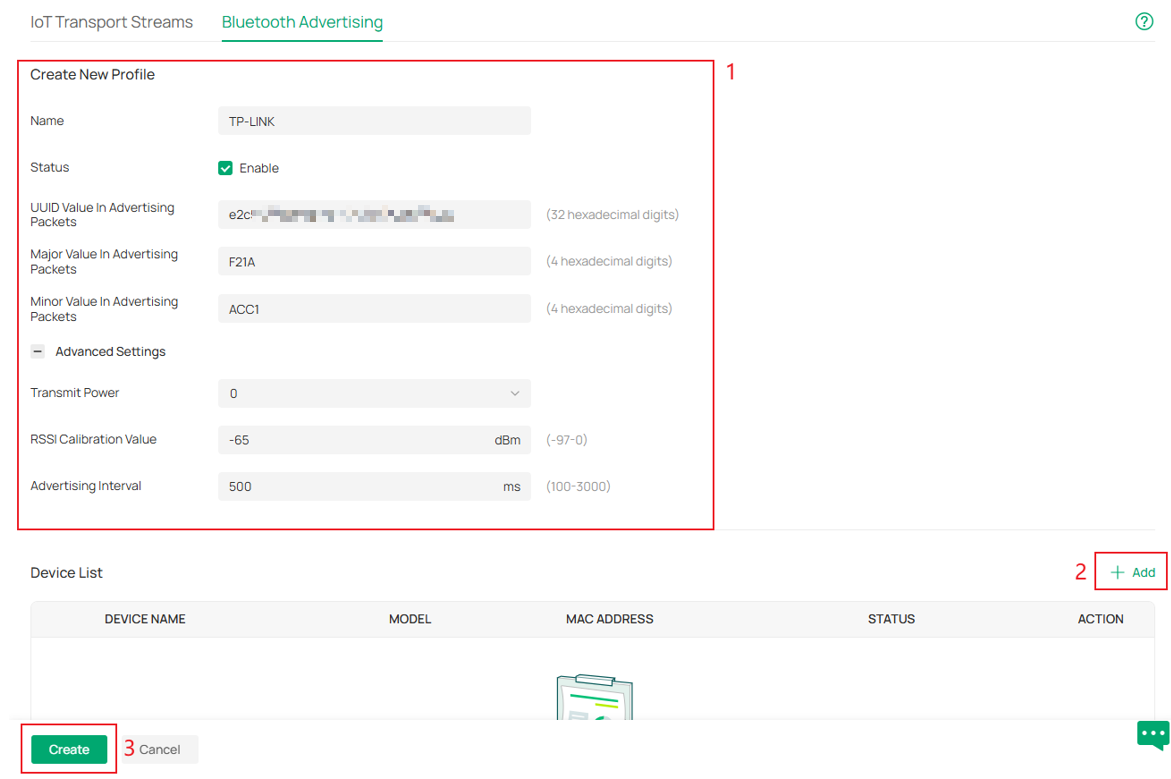
Parameters Explanation:
|
Item |
Configuration |
|
Name |
Enter a name to identify the profile. |
|
Status |
Enable or disable the profile. |
|
UUID Value In Advertising Packets |
The UUID (Universally Unique Identifiers) of the advertising iBeacon packet. (32 hexadecimal digits) |
|
Major Value In Advertising Packets |
The Major value of an advertising iBeacon packet, indicating a larger group. (4 hexadecimal digits) |
|
Minor Value In Advertising Packets |
The Minor value of an adverting iBeacon packet, indicating a smaller group. (4 hexadecimal digits) |
|
Transmit Power |
Broadcast transmit power (dB). The following values are currently supported: [-20, -18, -15, -12, -10, -9, -6, -5, -3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20] The higher the transmit power, the longer the coverage range. In actual deployment, ensure that the Bluetooth terminal receives the strongest Bluetooth signal from the nearest AP. Adjust this value according to the actual coverage to avoid interfering with the positioning of nearby APs. It is recommended that all APs use the same transmit power. |
|
RSSI Calibration Value |
-65dB by default. |
|
Advertising Interval |
Specify a value between 100 and 3000 ms. |
|
Device List |
The default Site-level entry does not feature this list. Only custom entries support configuration of specific devices. Currently, one Bluetooth Advertising profile can be configured for a single device. |
Step 3. Click Add to apply the newly added adverting profile to the specified EAP devices. In this way iBeacon frames sent by EAP in different areas can be inconsistent to distinguish the locations. As shown in the following figure:
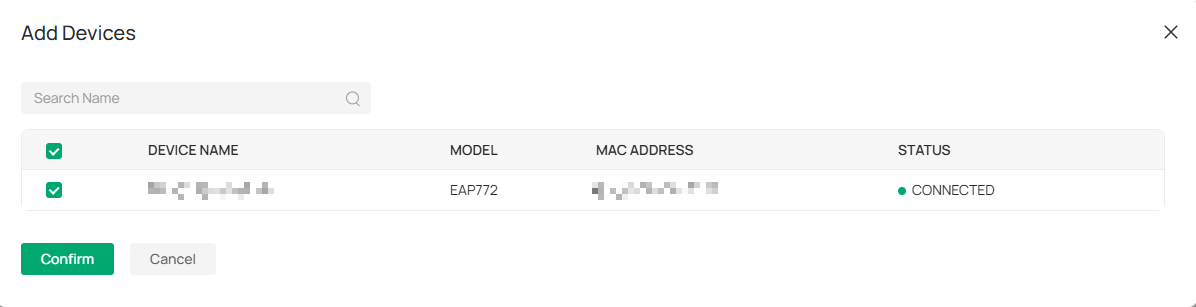
The configuration of IoT Transport Streams
By configuring the IoT Transmission Streams, AP can collect the required Bluetooth information and report it to a third-party IoT server. The network topology is as follows:
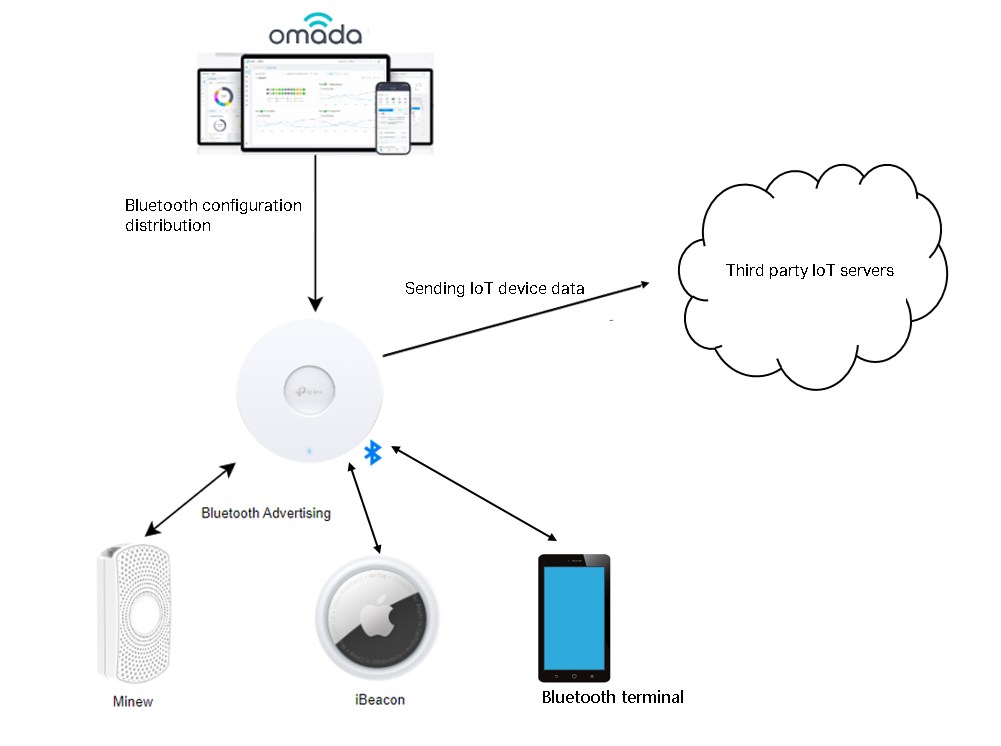
Step 1. Go to the Site View > Device Config > EAP > Bluetooth > IoT Transport Steams page.
On this page, you can configure rules for EAP to handle and report IoT data. It is Site-level configuration and all configuration will be applied to wireless devices on the current Site, and device-level configuration overrides are not supported.
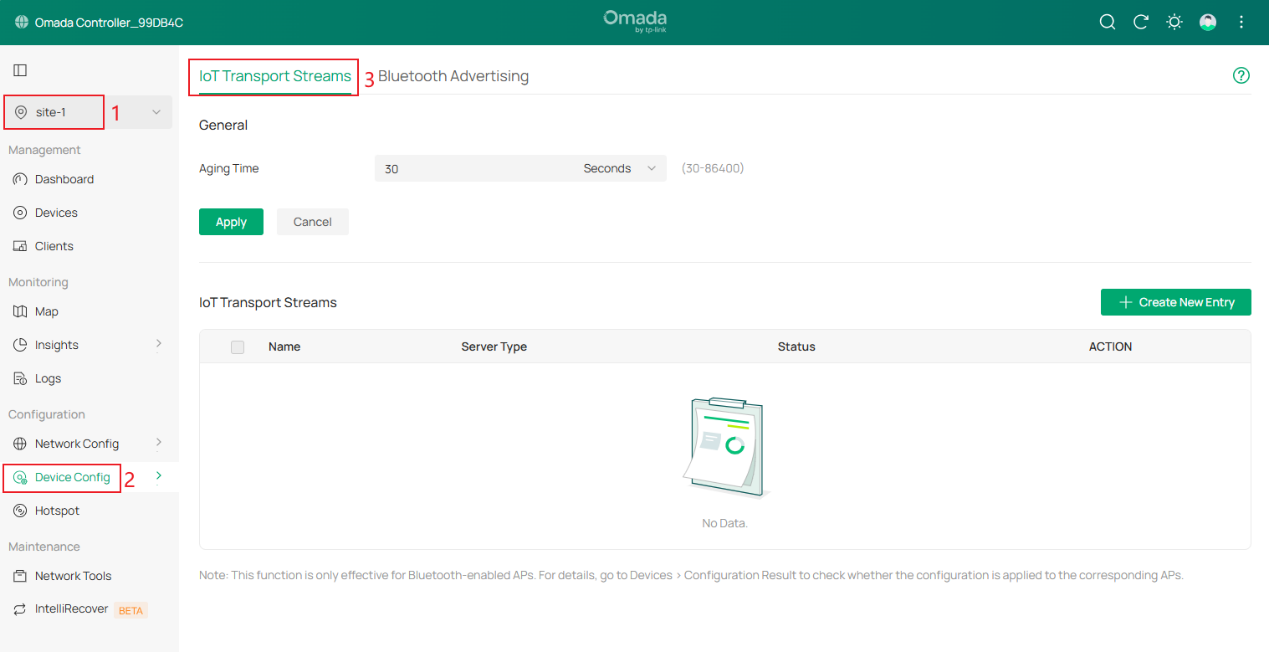
Step 2. Configure the Aging Time to control the device aging time.
In the General section, configure the Aging Time to control the device aging time. If no data is received from a device within a certain period, the entry for that device will be deleted. As a result, AP will no longer forward the data to the IoT server. If the AP receives data from that device again in the future, the device will be re-added, and its Bluetooth data will continue to be reported. The Aging Time can be configured in seconds, minutes, or hours.
Step 2. Click Create New Entry to configure the rules for the EAP to forward Bluetooth data. Up to 4 entries are currently supported.
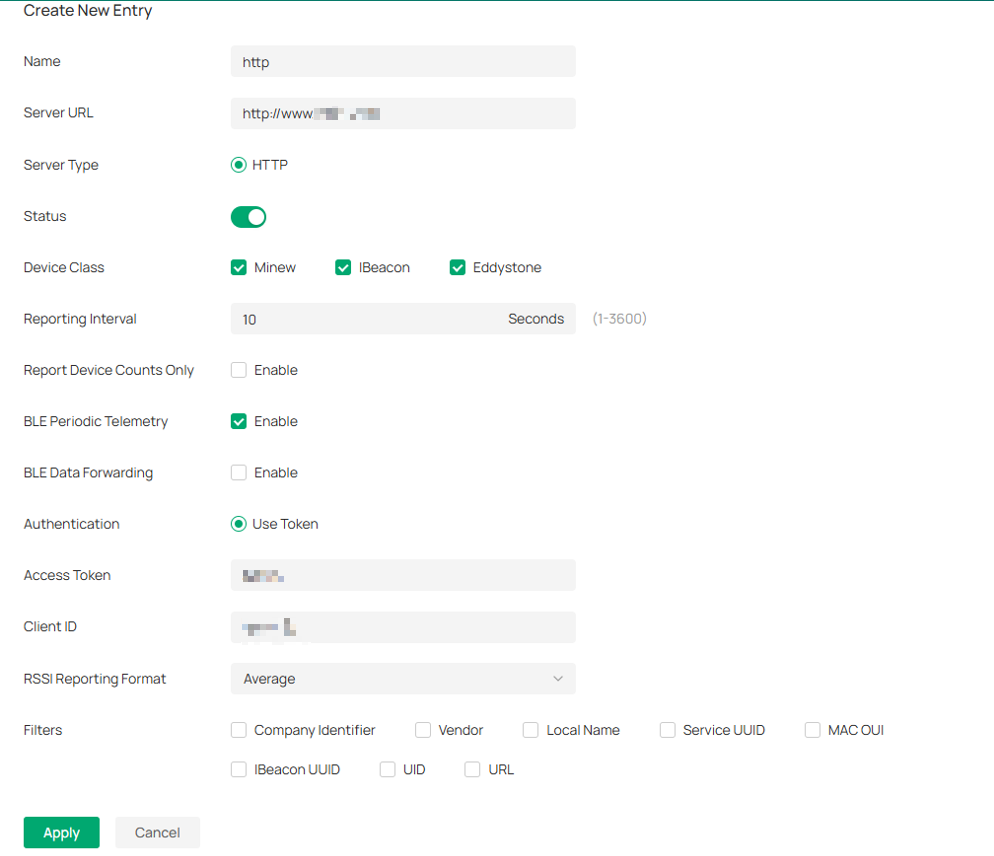
Parameters Explanation:
|
Item |
Configuration |
|
Name |
Enter a name to identify the profile. |
|
Server URL |
Enter the url of the third-party IoT server. URLs with http as the prefix are supported. |
|
Server Type |
Only http is supported. |
|
Status |
Where to enable or disable the entry. |
|
Device Class |
The supported manufacturers and protocols, ibeacon, Eddystone, and Minew |
|
Reporting Interval |
The reporting interval for the EAP to report IoT information. The shorter the interval, the better the real-time performance. |
|
Report Device Counts Only |
When enabled, EAP will only report the number of Bluetooth devices. Enable this feature if you just need to know the number of the Bluetooth device around EAP. |
|
BLE Periodic Telemetry |
It is enabled by default. When disabled, EAP will not periodically report IoT data. |
|
BLE Data Forwarding |
When enabled, AP will report the Bluetooth rawData to the server |
|
Authentication |
Refers to the authentication method of the server. Access Token: Indicates the token used for identity authentication. Client ID: Indicates the ID used for identity authentication. Authentication information is used for server authentication and establishing secure communication with the server. A legal token needs to be generated on the management side of the IoT server. |
|
RSSI Reporting Format |
Select the RSSI reporting format. There are five options, Average, Max, Last, Smooth, and Bulk.
|
|
Filters |
Custom the filters for EAP to filter IoT devices.
|
BLE Telemetry
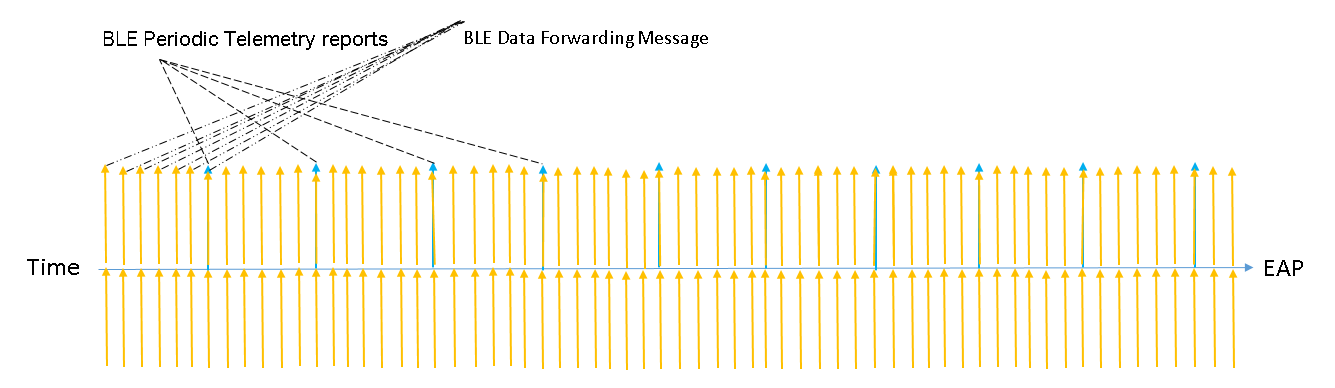
BLE Telemetry is a configuration of periodic reporting. When it is enabled, the AP will periodically report Bluetooth data according to the set interval. The AP will continuously collect Bluetooth information, interpret the data, and then report it in the specified format.
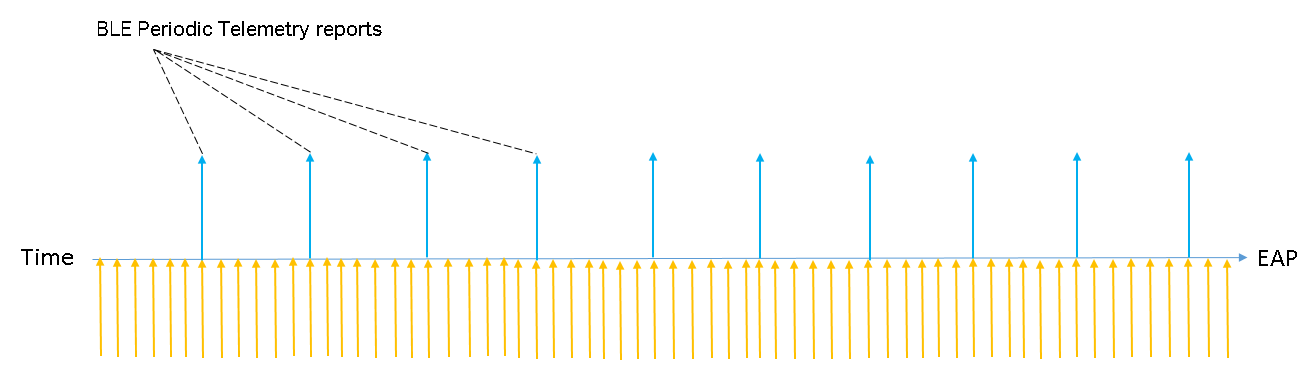
BLE Data Forwarding
When BLE Data Forwarding is enabled, the AP will automatically forward the BLE advertising frames of the specified protocols that it has collected. The data, the raw data received by the AP, is forwarded in real-time. Therefore, the forwarding frequency can also reflect the advertising interval of other Bluetooth devices. It should be noted that when BLE Data Forwarding is enabled, BLE Telemetry should also be enabled. If BLE Data Forwarding is considered as the primary mode, the reporting interval can be set higher. Furthermore, the Device Class selected in the IoT Transport Streams entry and the filter entry can also affect the data in Data Forwarding. The AP will filter the Bluetooth information based on these two filtering criteria before forwarding the data.
After completing the above configuration, you can view the Bluetooth data upload status on the third-party IoT Server page.
Parameter Optimization Recommendations
To achieve optimal Bluetooth performance, the following parameter optimization strategies are recommended:
- EAP Distribution Strategy
Positioning accuracy: To maximize positioning accuracy, mount EAPs below 3 meters high, keep 3–15 meters between each, and ensure at least three EAPs receive each Bluetooth tag message.
Maximum positioning distance: The theoretical range is 100 meters, but the recommended maximum distance between EAPs and clients is no more than 50 meters.
- Reporting Interval Parameter Configuration
1-10: For scenarios with high traffic volume or high real-time requirements.
10-60: For scenarios with medium traffic volume or moderate real-time requirements.
>60: For scenarios with low traffic volume or low real-time requirements.
Application Scenarios and Solutions
- Indoor Navigation
When EAPs (BLE or Wi-Fi) are deployed at stores, tourist attractions, or parking lots, and users use a mobile phone with Bluetooth enabled or Wi-Fi connected, the positioning server can collect data from the EAP to calculate the location.
The management platform displays user density, itineraries, and other information. The positioning server provides the location data to third-party applications, such as maps, through an open API, facilitating user location tracking.
- Asset Location Management
By fixing the BLE tags on the assets to be tracked and deploying EAPs that can receive iBeacon frames in the office area, the EAPs can report the collected RSSI information to the positioning server, and the asset can be located and tracked through the mobile management application.
- Personnel Management and Tracking
When the BLE tags are attached to the wrists of personnel or charges (such as patients) and EAPs that can receive iBeacon frames are deployed in the designated area, the EAPs can upload the collected information such as RSSI to the positioning server, allowing the management platform to monitor the collective location and movement trajectory of the personnel and charges.
- Geofencing
When employees attach the BLE tags to their wrists or users hold the mobile terminal, and EAPs are deployed in the working area, the positioning server can collect data, such as RSSI, from the EAPs to calculate the user location.
Conclusion
By following the steps above, you can know how to configur Bluetooth IoT positioning feature successfully.
FAQ
Q1: Common Problems and Troubleshooting
A1:
|
Problems |
Possible Cause |
Troubleshooting |
|
The parsed location information is null |
The Bluetooth client’s communication protocol does not currently support parsing the information. |
Enable BLE Data Forwarding to check if the transmitted data contains location information. |
|
The positioning is inaccurate. |
Severe interference |
Check the EAP location and transmit power configuration. |
|
The location is updated slowly |
Long report interval and high EAPserver latency |
Verify the Report Interval configuration and the connection between the EAP and the server |
Get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.