Contents
Configuration for mDNS Rules on Newly-added APs
Configuration for mDNS Rules on Newly-added Gateways
Configuration for mDNS Rules on APs with Custom Services
Objective
This article introduces how to configure the mDNS function on the Omada gateways and APs via the Omada Controller.
Requirements
- Omada Software Controller / Hardware Controller / Cloud-Based Controller
- Omada Gateways / APs
Introduction
mDNS: a DNS service discovery protocol based on IP multicast, is designed to automatically discover and resolve services within a local area network. It is mainly used in small networks without a centralized DNS server, such as home networks or small office networks.
The mDNS client queries service information by sending a request to IPv4 address 224.0.0.251 or IPv6 address FF02::FB, while the mDNS server monitors this multicast address and returns the service information it provides to the client.
mDNS identifies services using the domain name with a special format, such as "printer_ipp_tcp_local". When a device attempts to access a service, it resolves the domain name through mDNS to obtain service information including the IP address and port number.
Bonjour: An mDNS-based service discovery protocol developed by Apple. When a Bonjour-compatible device joins the network, it will use mDNS to broadcast the service information it provides to the local network. Other Bonjour-compatible devices will discover available Bonjour services in the network by listening to mDNS broadcasts.
Configuration
In Controller mode, the mDNS repeater can forward mDNS request/reply packets among different VLANs. Therefore, you can create forwarding rules to allow devices in a VLAN to which the specified clients connected to discover the mDNS service in a specified service VLAN, as well as specifying the type of service to forward.
Configuration for mDNS Rules on Newly-added APs
Step 1. Log in Controller, go to Network Config->General Settings->mDNS to load the following page.
Step2. Click Create New Rule to create a new mDNS rule, and then specify the corresponding parameters: enter the rule name (new_rule for example), and check Enable to enable the rule status. Device Type is the type of device to which the rule will be applied (here, we choose AP). Bonjour Service is the service type that supports request forwarding, such as AirPlay. Services Network specifies the VLAN where the mDNS service is located via the VLAN ID, while Client Network specifies the VLAN where the client is located via the VLAN ID. For both items, you can enter the VLAN range or VLAN ID separated by commas, such as 1, referring to the default LAN.
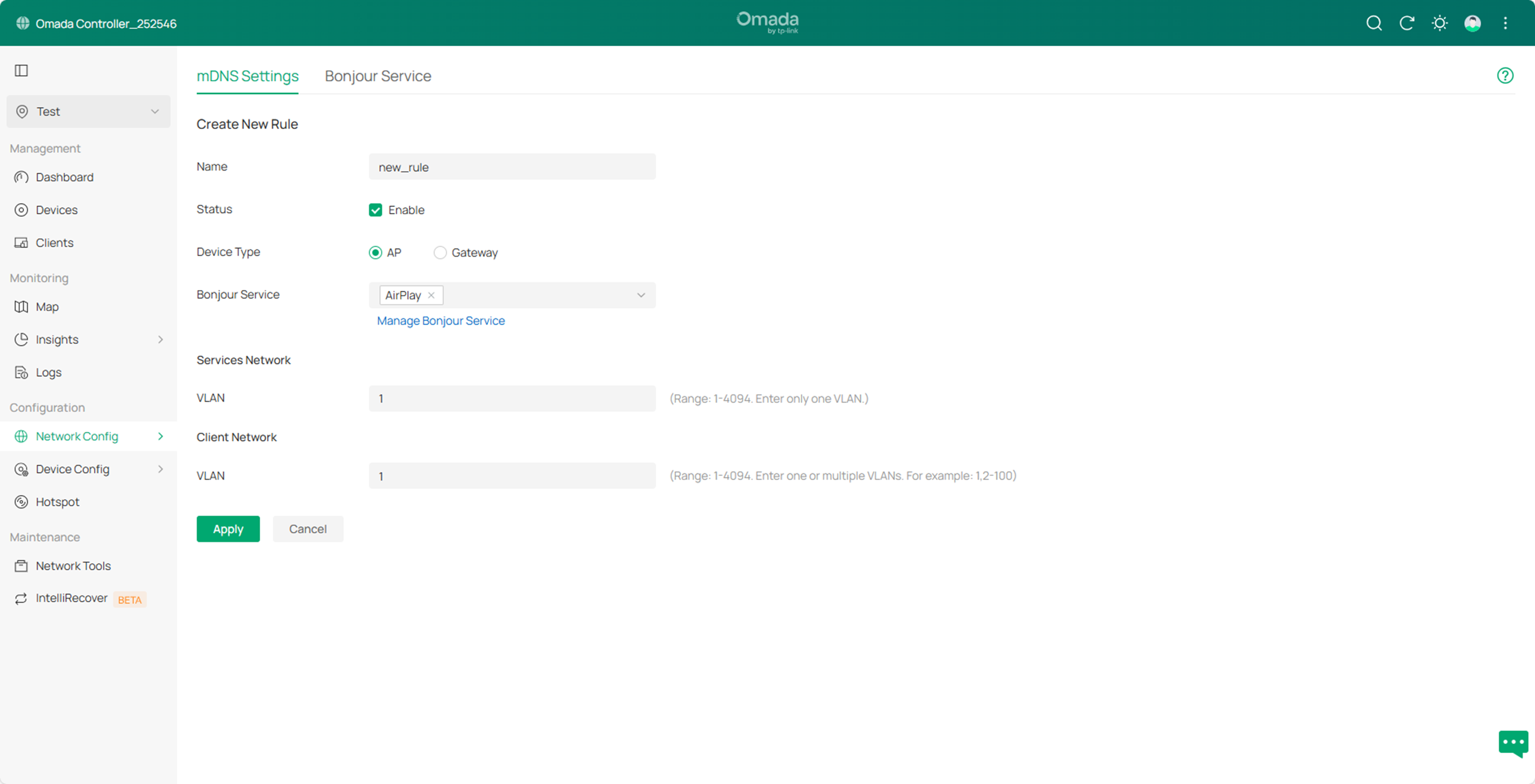
Step3. Click Apply to save the configuration.
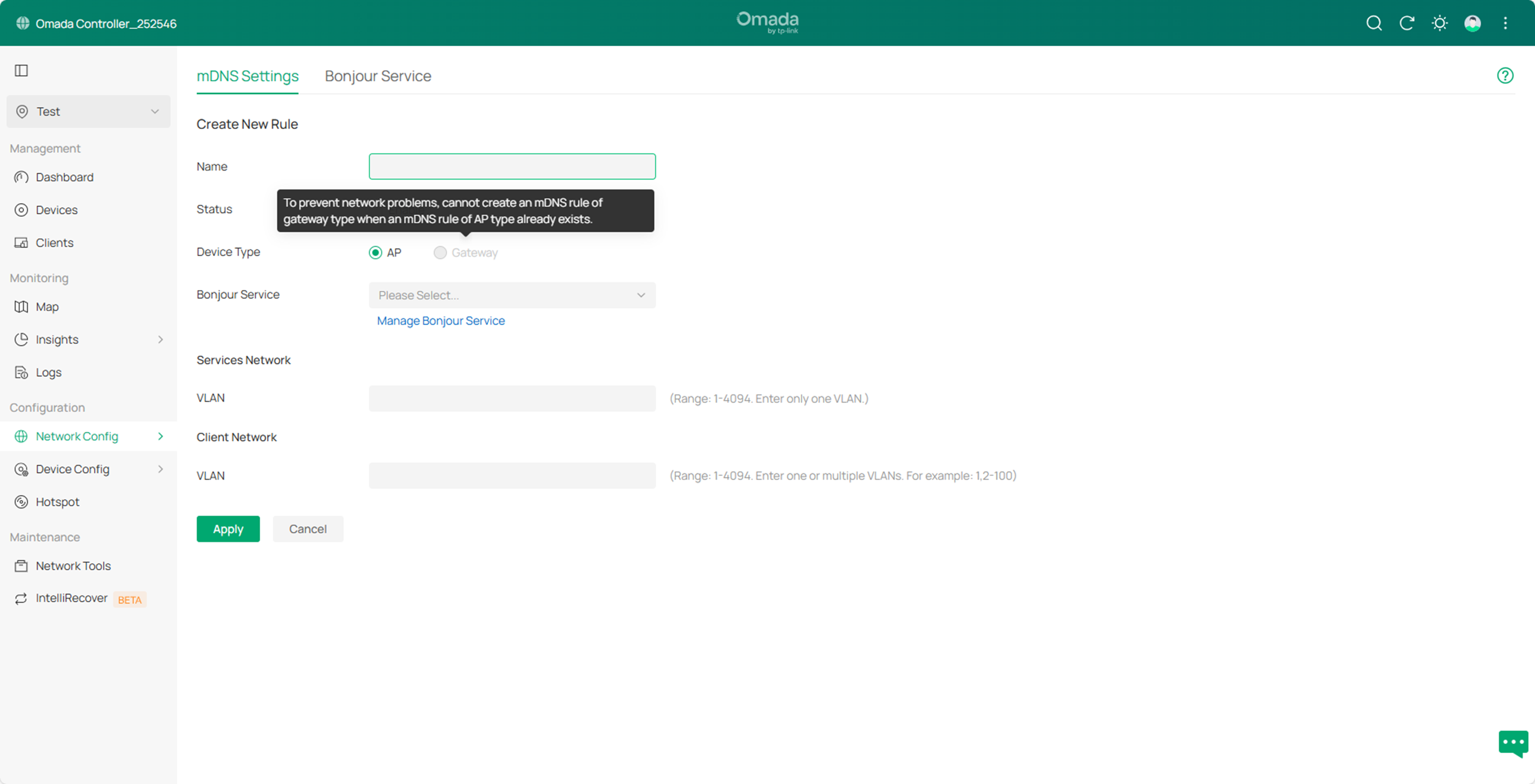
Note: To avoid network problems, when an mDNS rule for APs already exists, only new mDNS rules for APs can be created. The same applies when an mDNS rule for gateways exists.
Configuration for mDNS Rules on Newly-added Gateways
Step1. Log in Controller, go to Network Config > General Settings > mDNS to load the following page.
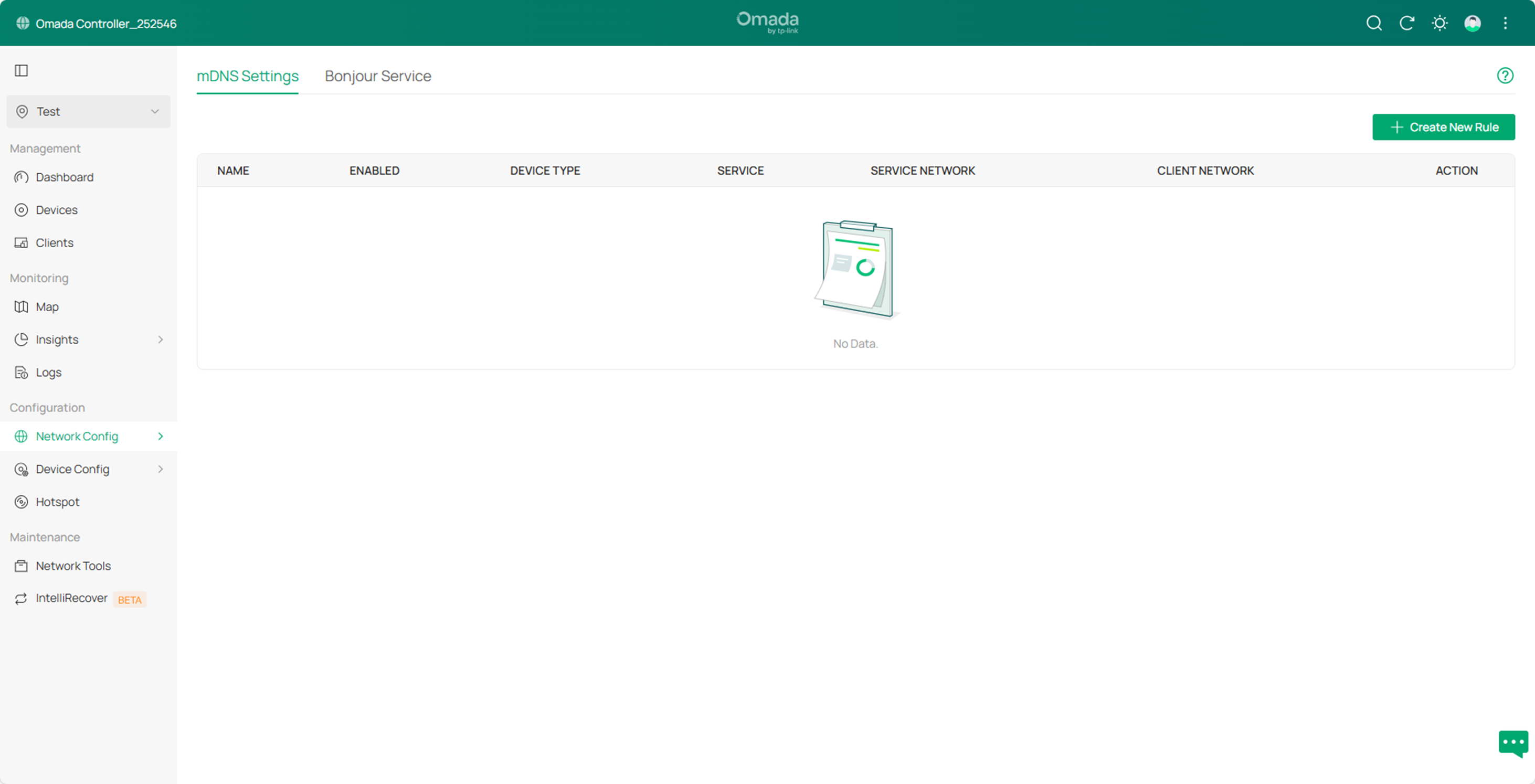
Step2. Click Create New Rule to create a new mDNS rule, and then specify the corresponding parameters:
- Enter the rule name (new_rule, for example);
- Check Enable to enable the rule status;
- Device Type is the type of device to which the rule will be applied (here we choose Gateway);
- Bonjour Service is the service type that supports request forwarding, such as AirPlay;
- Services Network specifies the network segment where the mDNS service is located by selecting the LAN configured by the current Controller. The example is Default, indicating the default LAN;
- Client Network specifies the network segment where the client is located by selecting the LAN configured by the current Controller. The example is Default, indicating the default LAN.
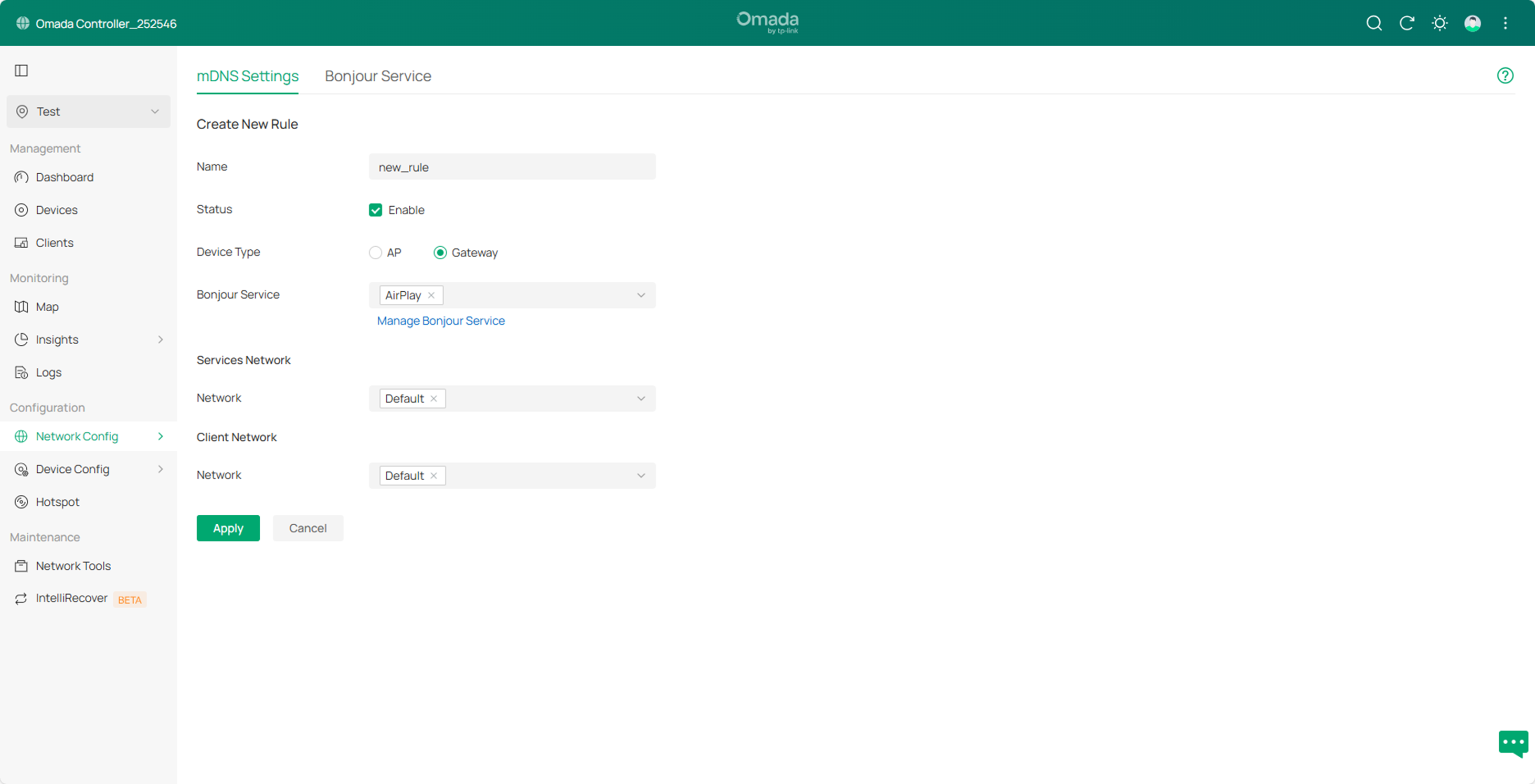
Step3. Click Apply to save the configuration.
Configuration for mDNS Rules on APs with Custom Services
Step1. Log in Controller, go to Network Config > General Settings > mDNS to load the following page.
Step2. Click Bonjour Service. On this page, you can view the built-in services of the current system and configure custom services.
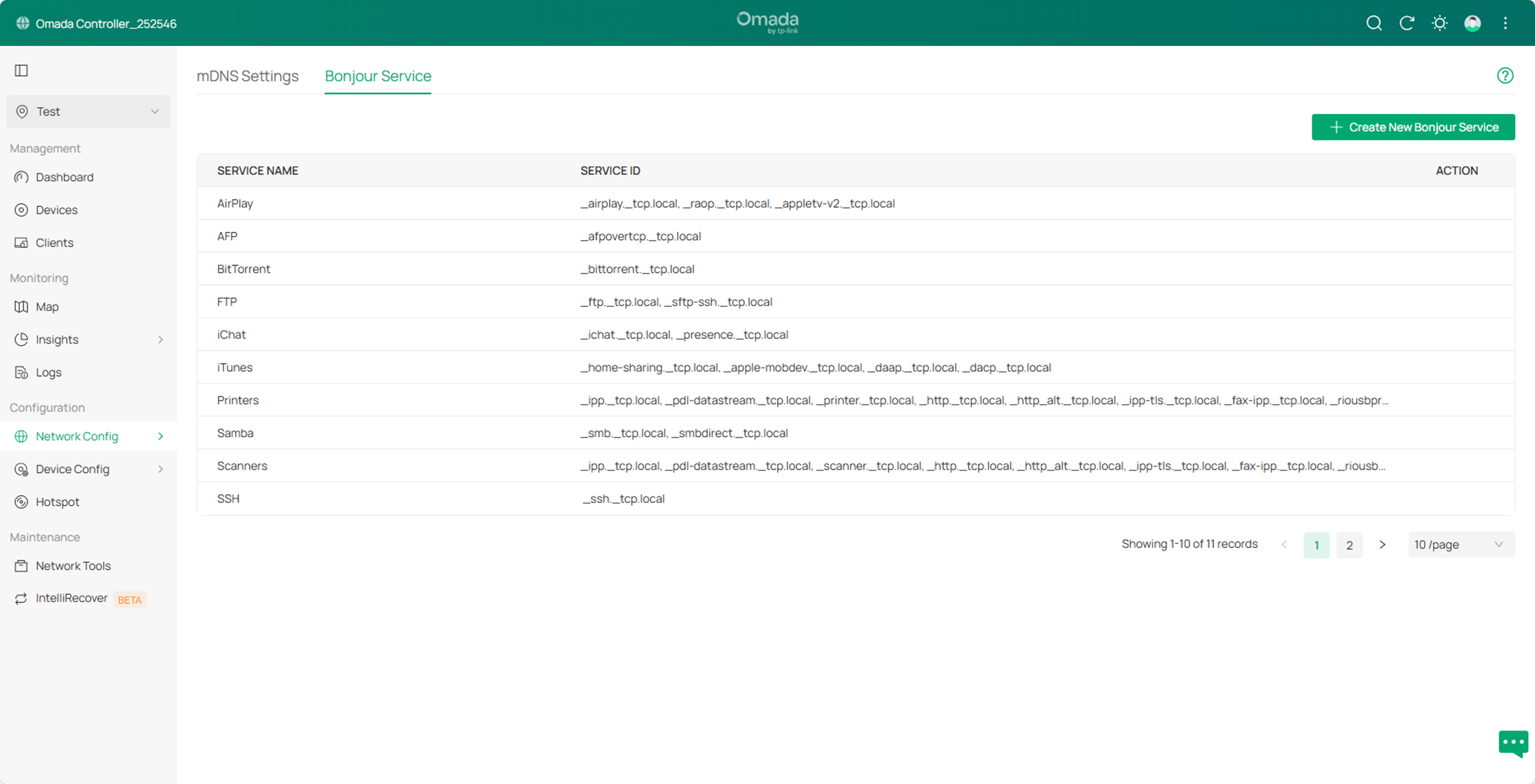
Step3. Click Create New Bonjour Service to create a new service and specify the service name and ID.
- For Service Name, enter a custom name, e.g. iot.
- For Service ID, multiple IDs can be configured, and the example here is "_iot-http._tcp.local". See FAQ for the details of Service ID format.
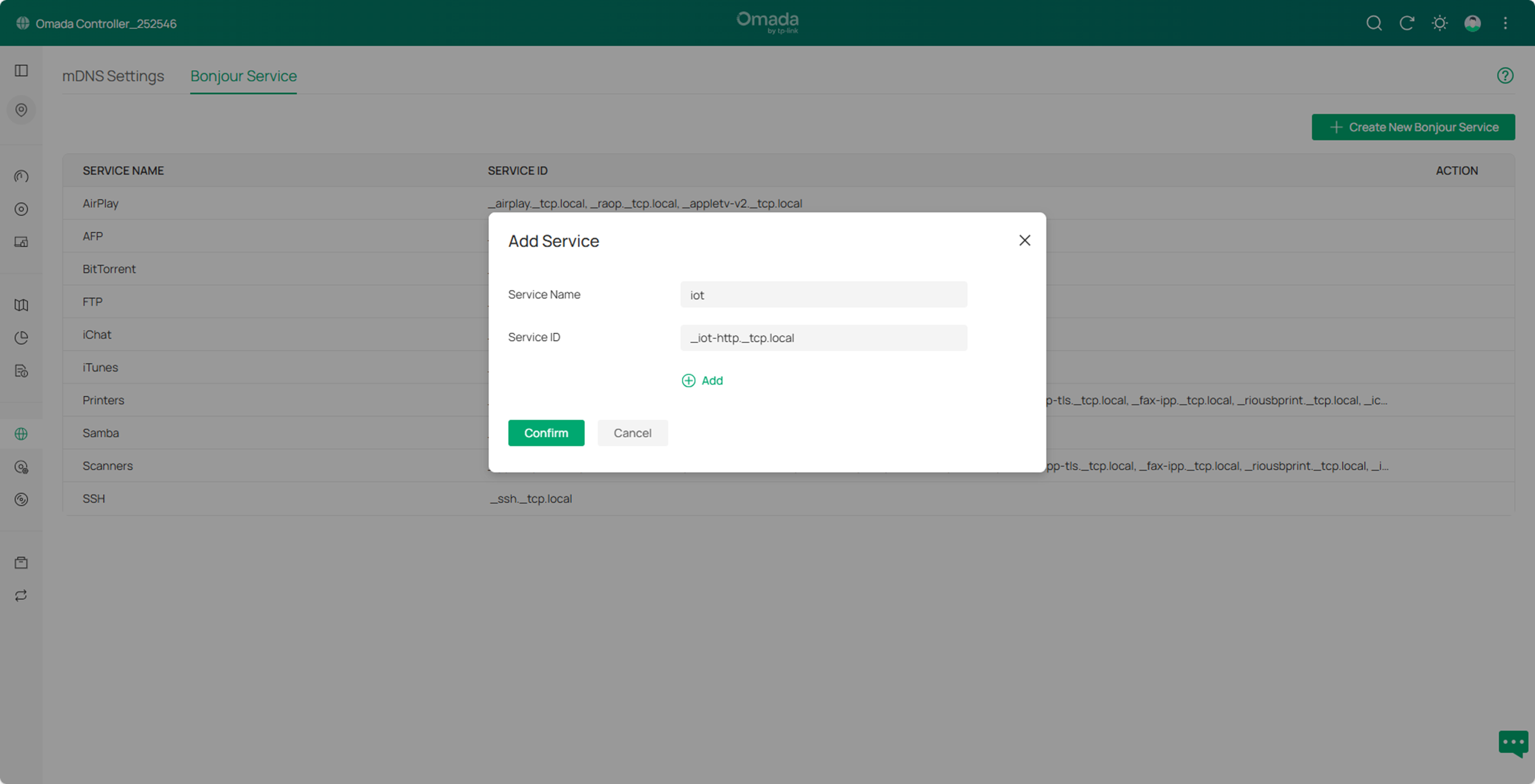
Then click Confirm to save the configuration.
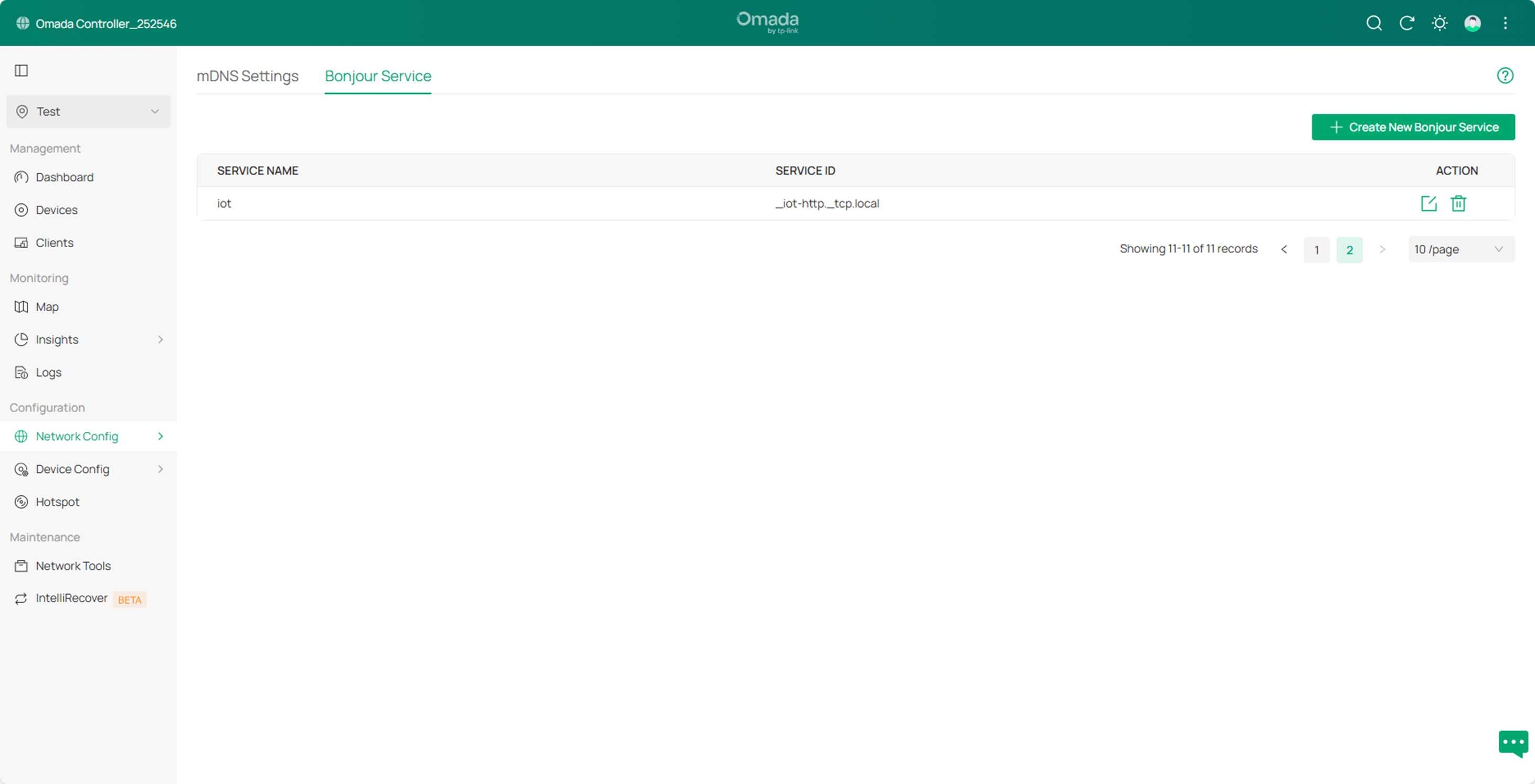
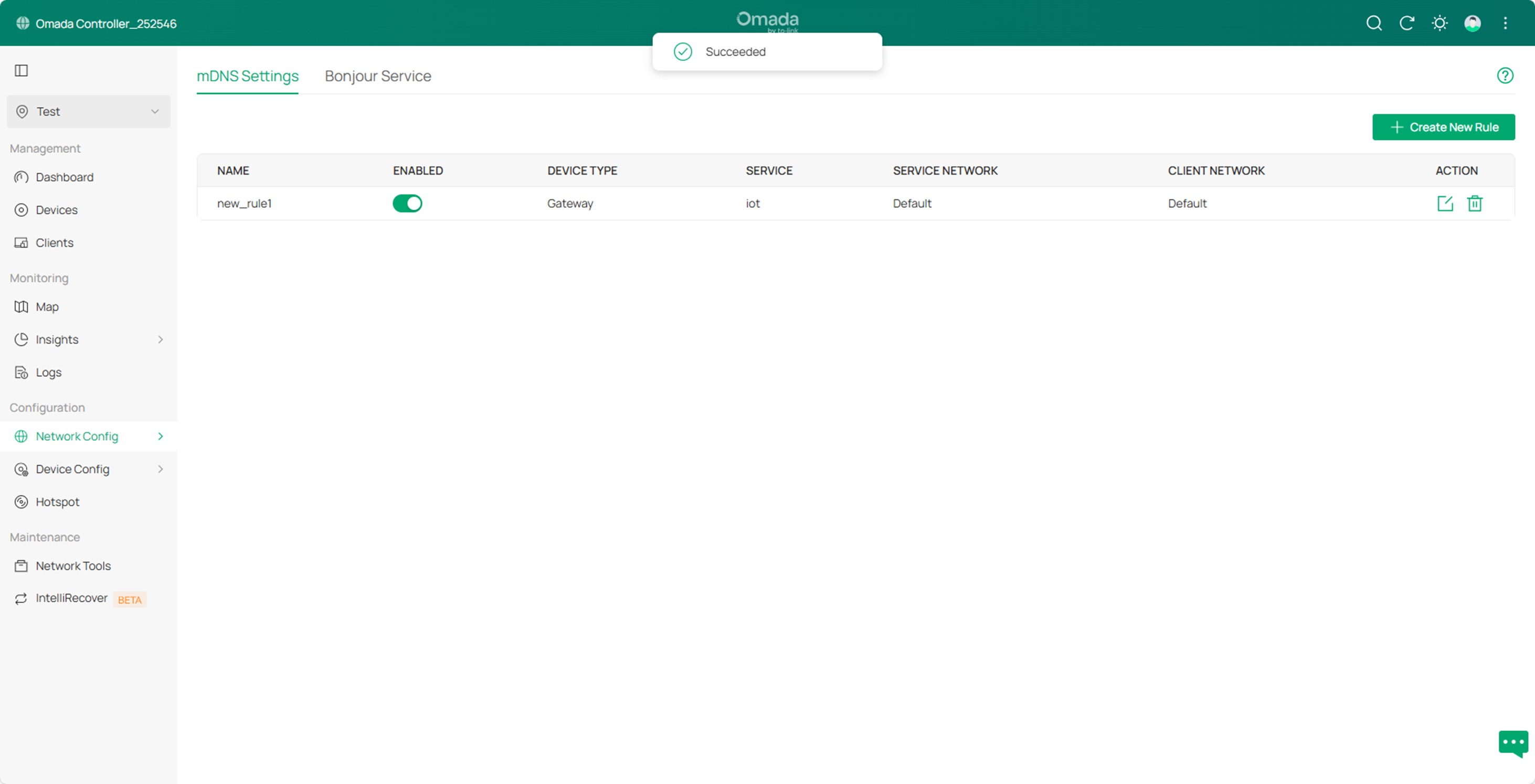
Step4. Go to Network Config->General Settings->mDNS, then click Create New Rule to create a new mDNS rule. For Bonjour Service, select the newly created service type iot.
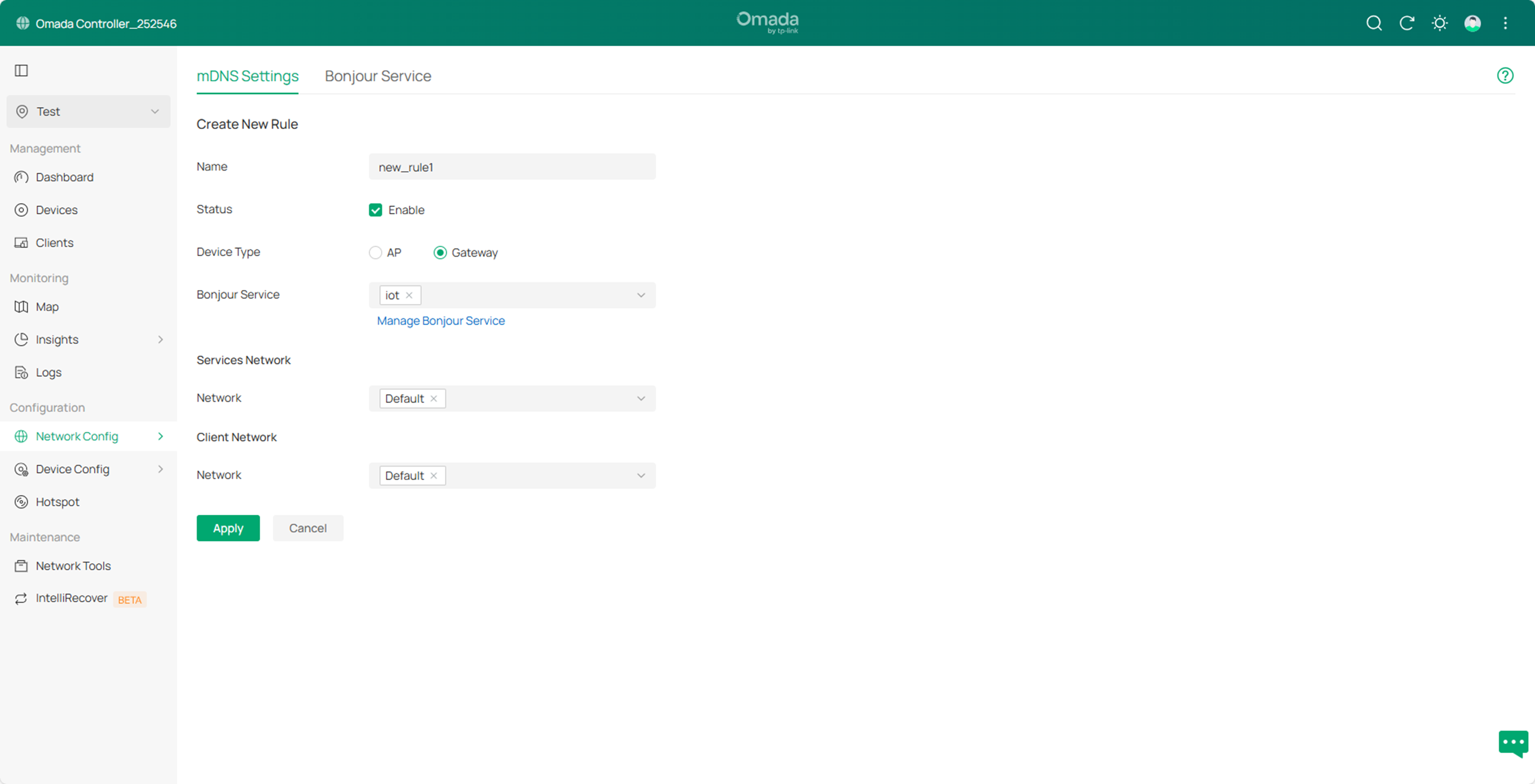
Click Apply to save the configuration.
Conclusion
Follow the guide above, you can configure the mDNS function of Omada gateways on the Omada Controller.
To get more details of each function and configuration, please go to Download Center to download the manual for your product.
FAQ
1. What is the format of a new service domain name?
Re. The domain name format supported on the Omada Controller is:
_<service-type>._<transport-protocol>.local
The meaning of each part is as follows:
- ._<service-type>: Service type identifier, starting with an underscore _, followed by the service type name. For example, _http, _ftp, _printer, _scanner, etc.
- ._<transport-protocol>: Transport protocol identifier used to indicate the network transmission protocol used by the service, usually ._tcp or ._udp.
Note: When configuring a service domain name in the Omada Controller, a suffix ".local" is required.
·local: The local domain name suffix, indicating that this is a service within the local area network. Bonjour uses .local as the local domain name suffix by default.
2. How do you query the official Bonjour service type identifier registry?
Re: IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) coordinates an official global service type identifier registry. You can check the registered standard service types on the IANA website: https://www.iana.org/assignments/service-names-port-numbers/service-names-port-numbers.xhtml.
In addition to the IANA website, the following options are available:
- Apple's Bonjour development documents. As one of the main promoters of the Bonjour protocol, Apple lists many commonly used service type identifiers in their Bonjour development documents. You can search relevant documents on Apple’s Developer website: Apple Developer
- RFC documents of IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force), the leading organization for Internet standardization. Some of the RFC documents released by IETF also provide relevant specifications for service type identifiers, for example, RFC6763 "DNS-Based Service Discovery".
- Open source projects and community documents. Some open source Bonjour/Zeroconf implementation projects, such as Avahi, Bonjour for Windows, etc., also list commonly used service type identifiers in their development documents or official websites.
- Industry standards and specifications. Some specific industries may develop their own service type standards. For example, the IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) of the printer industry includes relevant service types.
- Service provider's documentation. If you need to use the service type of a specific service, you can refer to the documents from the service provider, which usually contain the corresponding service type identifiers.








