Contents
Objective
This article introduces how to help you improve wireless performance by configuring Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit to save Air Interface resources and reduce interference.
Requirements
- Omada Software Controller / Hardware Controller / Cloud Based Controller version 5.14 or above
- Omada AP, such as EAP 660, EAP 655-wall
Introduction
In large or medium-sized networks with a high number of devices, or in environments where users frequently utilize multicast services such as IPTV, video conferencing, live streaming, or service discovery protocols like Apple's Bonjour, the number of multicast packets in the wireless network significantly increases.
If there are too many Multicast messages, redundant information in the network increases, and truly important information (Unicast data, such as web pages or videos) may be squeezed for bandwidth. Limiting Multicast rates can prevent useless broadcasts from overwhelming normal traffic and reduce network congestion.
In wireless environments, a high volume of multicast packets can lead to a congested or "dirty" airspace, resulting in degraded performance and increased interference.
In Wi-Fi networks, Multicast traffic is transmitted at low data rates, consuming excessive airtime and affecting all clients, even those not intended to receive the packets. Frequent types of multicast packets include mDNS, SSDP, IGMP, ARP. To maintain wireless performance, Reducing the Multicast/Broadcast rate can make the wireless air interface more efficient and improve the internet experience for end devices.
Configuration
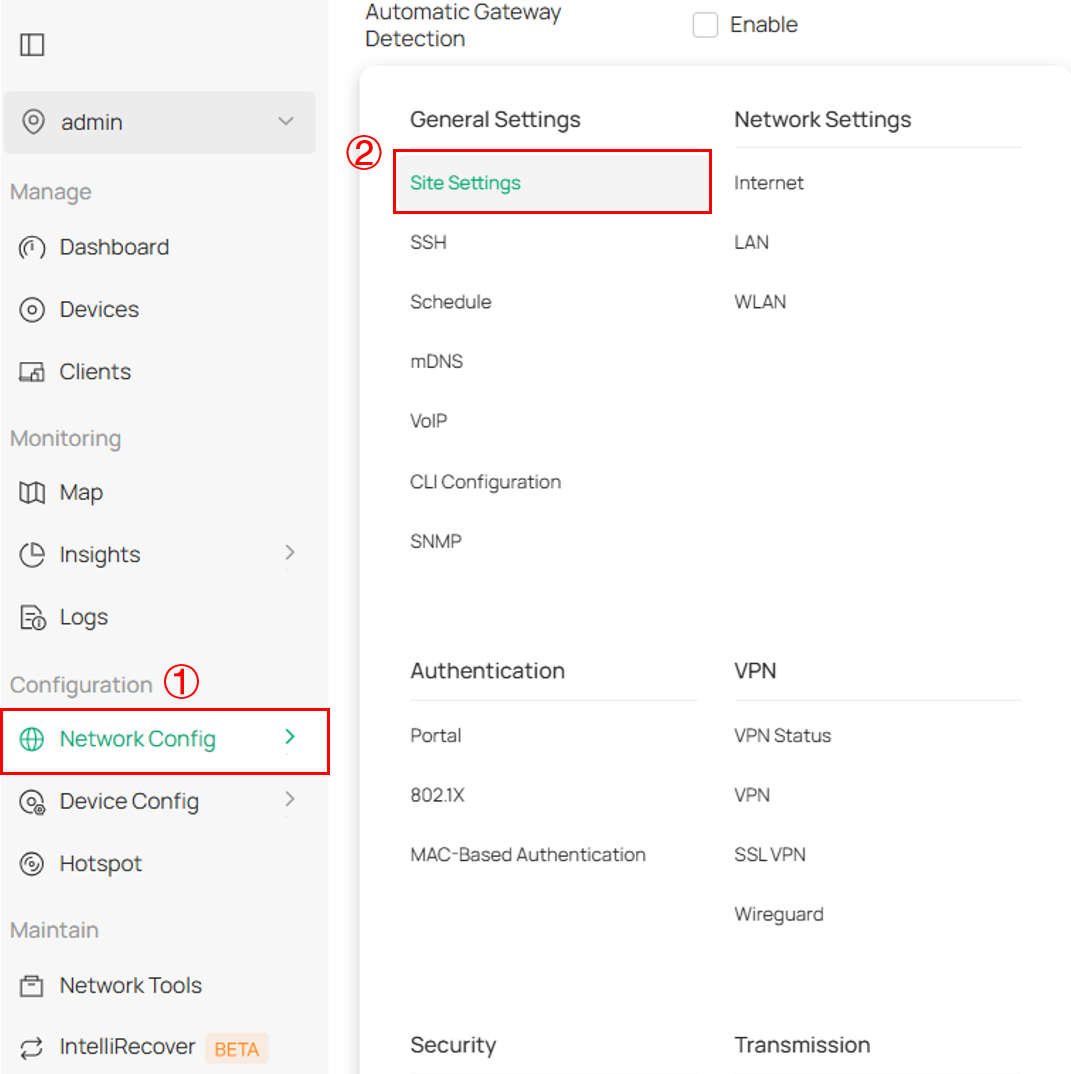
Step 1. Log in to the Controller Web Page, and switch to the Site view, Navigate to Network Config > Site Settings.
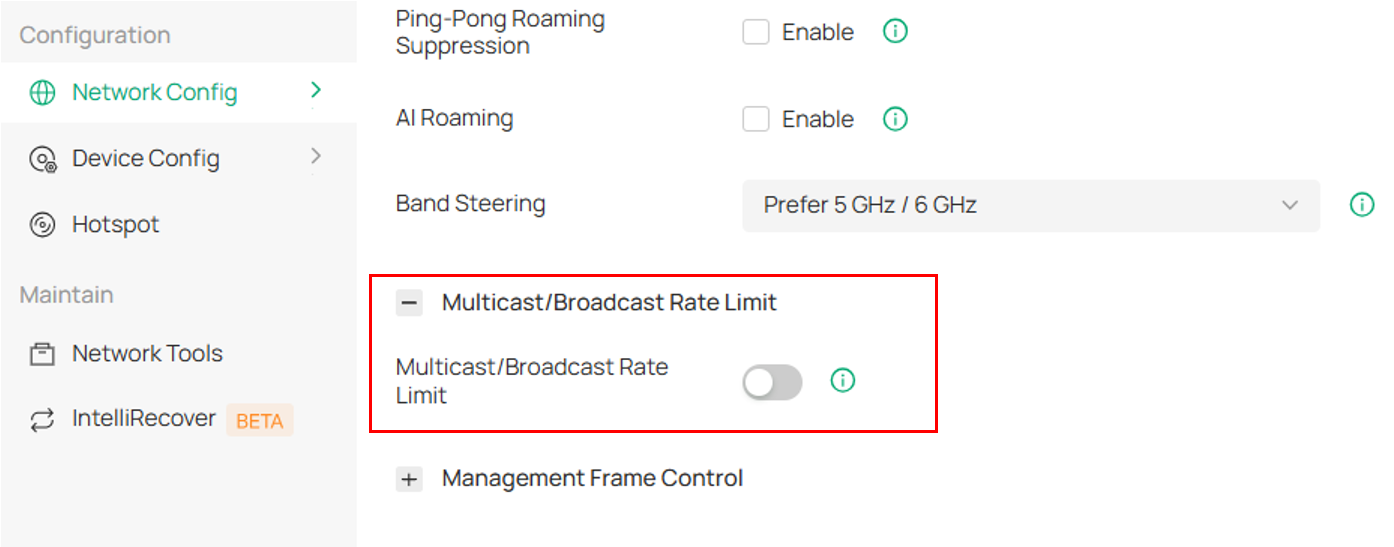
Step 2. Enable Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit in Site Settings
Step 3. Configure the rate limit for Multicast/Broadcast messages.
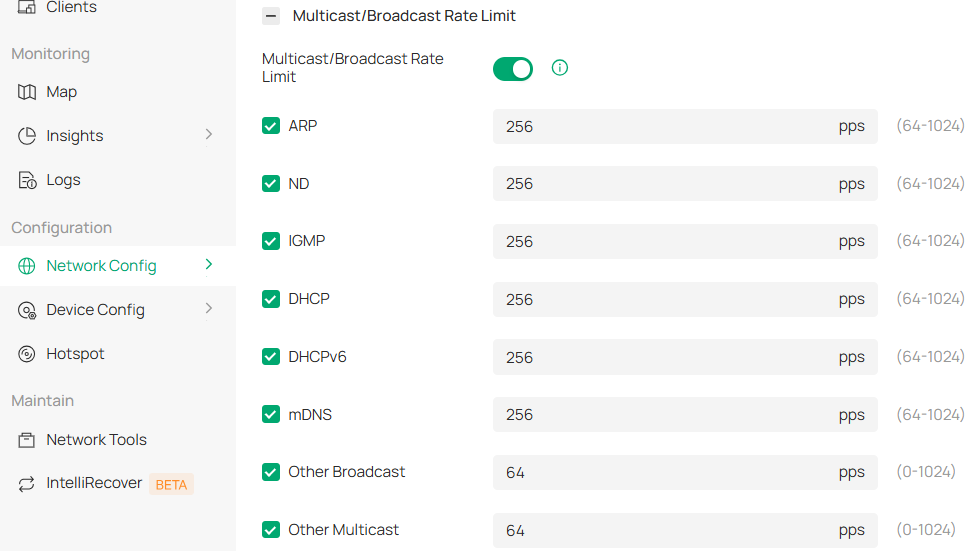
Note: The rate limit for each type of Multicast/Broadcast message can generally be set to the default value. For ARP, ND, IGMP, DHCP, DHCPv6, and mDNS packets, the speed limit ranges from 64 to1024 pps, with a default value of 256 pps. “pps” means “Packets Per Second”. For other Broadcast and Multicast packets, the speed limit ranges from 0 to 1024 pps, with a default value of 64pps.
If you want to further understand the role of each Multicast/Broadcast message and how to configure pps values, please refer to the FAQ below. If the user is not an expert in the field of networking, it is recommended that they maintain the default settings.
Verification
Help you verify if the function is effective.
Step 1: Download Colasoft Packet Builder free edition in Packet Builder for Network Engineer - Colasoft and Wireshark in Wireshark • Go Deep
Step 2: Open Colasoft Packet Builder, Click Add to create a Multicast packet, using ARP as an example.
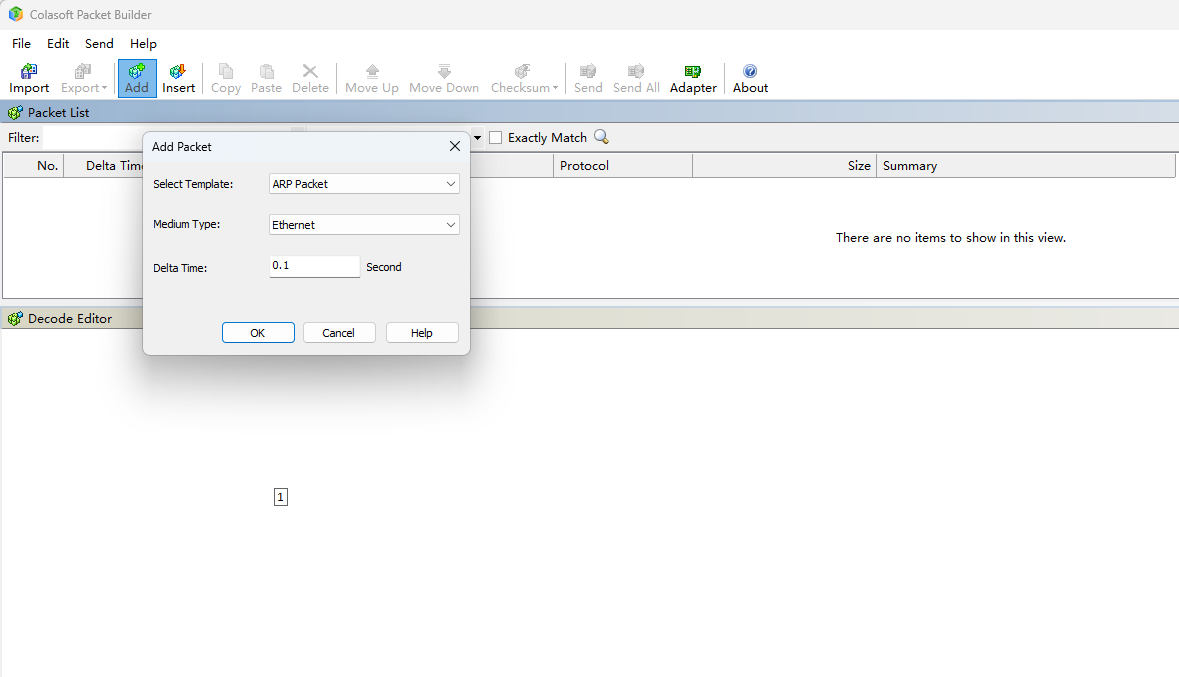
Modify the source MAC address of the Multicast packet to the MAC address of the network adapter that will actually send it.
Note: The network adapter needs to be on the LAN side of the device, and Multicast/Broadcast rate is limited to packets sent from the LAN side to the WLAN side.
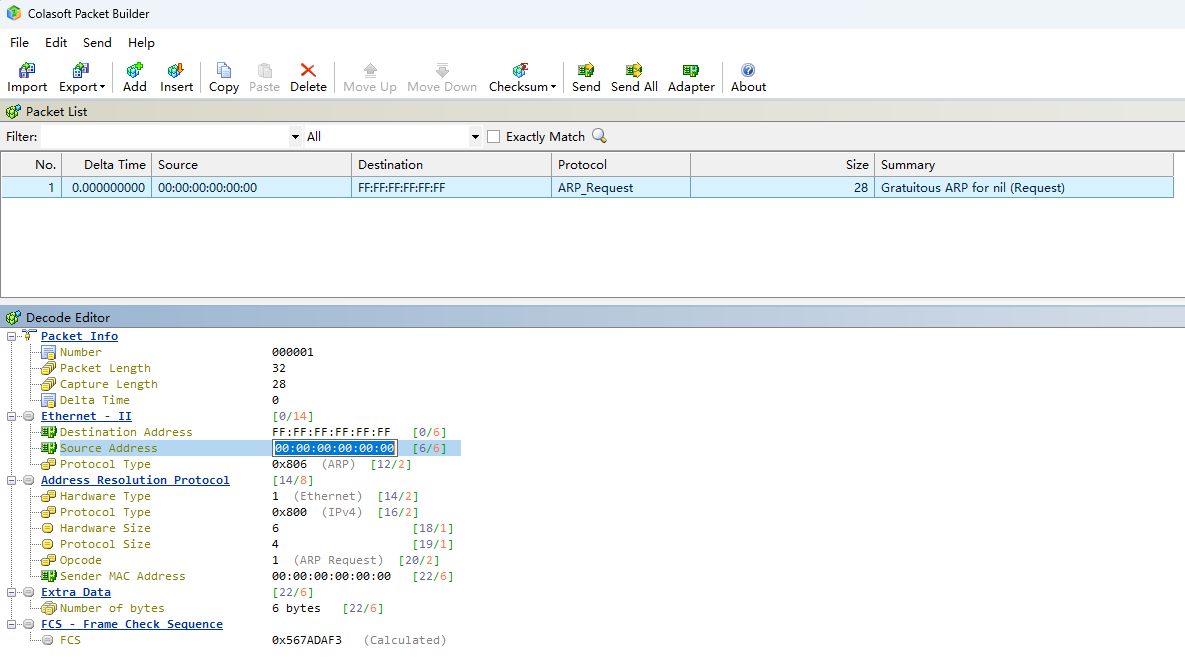
Step 3: After finishing the modifications, right-click and select Send selected packets.

Step 4: Select the network Adapter to send.
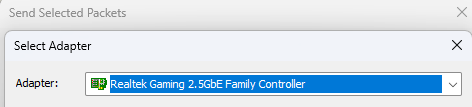
Note: If the corresponding network adapter cannot be detected, try reopening the software as an administrator.
Step 5: Choose the sending mode.
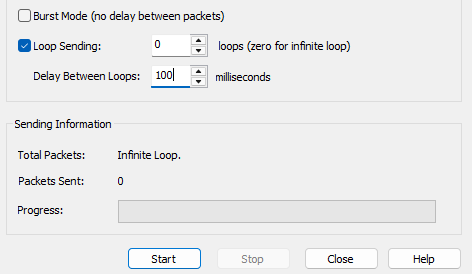
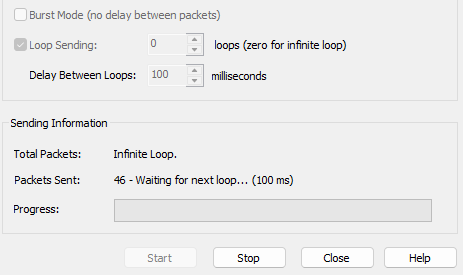
Step 6: Click Start. The Multicast packets will be sent.
Step 7: Go to Site>Devices in Omada Controller. Select an AP, click Manage Device>Tools>Packet Capture, Capture the packets from wireless interfaces or bkhap.
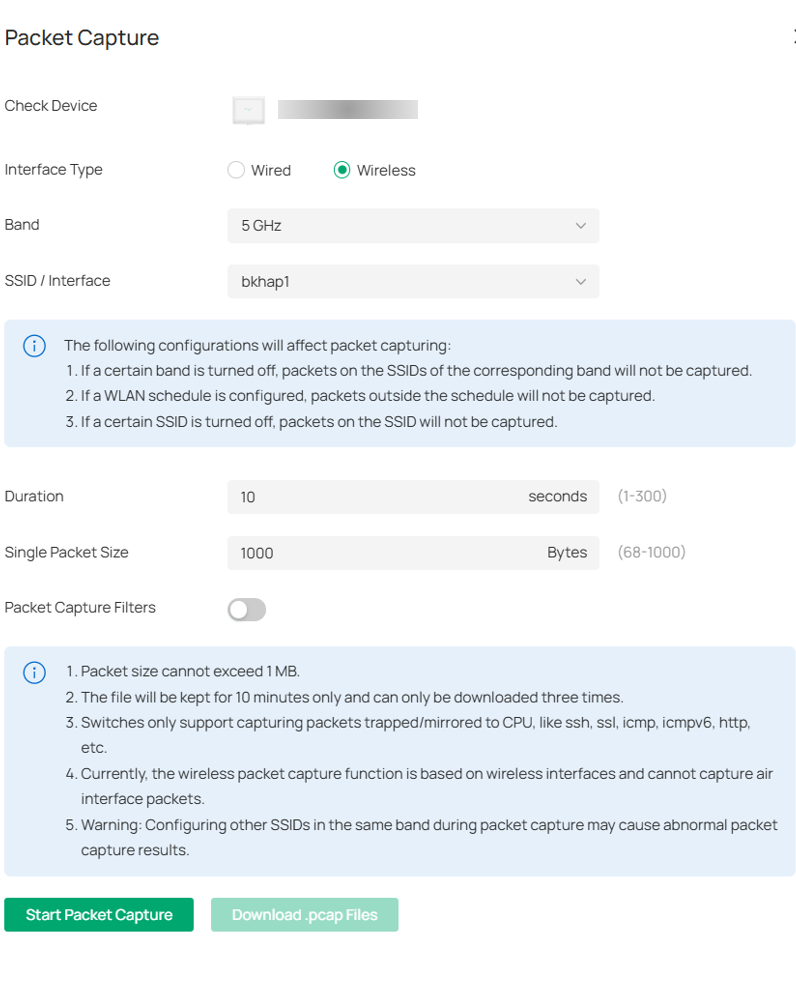
Step 8: Download .pcap File and then open it with Wireshark. Check the number of captured packets within the time frame, which should be less than or equal to the theoretical maximum Multicast packet rate limit.
Conclusion
Following the steps above, you can configure and verify the Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit function.
FAQ
1. How to check if the AP supports this feature?
Answer:
Go to Devices>Configuration Result>Incompatible to check if your AP device support Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit.

2. When should the “Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit” function be enabled?
Answer:
It is recommended to choose the appropriate PPS value based on the number of Multicast/Broadcast packets in the network and the current channel utilization situation. Some scenarios are as follows.
·High-Density Environments: Such as conference rooms, classrooms, exhibition halls, airports, etc., where many users connect simultaneously.
·Multimedia Streaming or Video Multicast Scenarios: Used in IPTV, online education, remote conferencing, etc., where Multicast is common.
·Wireless Network Performance Optimization: Broadcast/Multicast packets are typically sent at low data rates over Wi-Fi, reducing overall throughput.
In addition, you can refer to the multicast traffic statistics chart. Go to Devices>Manage Device>Statistics.

3. What is the function of each message type under this module of “Multicast/Broadcast Rate Limit”? How to configure their values?
Answer:
ARP(Address Resolution Protocol): Help devices discover the MAC address associated with a specific IP address, enabling data to be sent to the correct destination on the network. It is not recommended to set pps to a small value, otherwise it may affect the device's ability to obtain the MAC address.
ND(Neighbor Discovery Protocol): Used in IPv6 networks for devices to identify the addresses and status of neighboring devices. It functions similarly to ARP but is specifically designed for IPv6. If there is no IPv6 address in the network, it can be set to the lowest value.
IGMP(Internet Group Management Protocol): It allows devices to inform routers that they wish to join a specific multicast group, commonly used in services like IPTV and live video streaming. At a low pps value, the transmission of IPTV/video streams will be affected.
DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Automatically assigns IP addresses to devices connecting to an IPv4 network. It is not recommended to set the pps too low, as it may cause difficulties in obtaining IP addresses for devices, unless all devices in the network are assigned static addresses
DHCPv6(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6): Performs the same function as DHCP but in IPv6 networks, assigning addresses to IPv6-enabled devices. If there is no IPv6 address in the network, it can be set to the lowest value.
mDNS(multicast Domain Name System): Enables devices within a local network to discover and communicate with each other without relying on a traditional DNS server. It is frequently used in wireless screen mirroring and Apple device data transmission. If there is no similar scenario in the network environment, it can be set to the lowest value.
Other Broadcast: Loop Detection Messages, etc.
Other Multicast: SSDP(Simple Service Discovery Protocol), LLMNR(Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution), etc.
Get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.








