Brief introduction about VLAN topology in Omada Network v6
Contents
Getting device information and customizing your topology
Filtering and highlighting devices in the network topology
Introduction
This FAQ introduces some tips and highlights about VLAN topology in Omada Network v6.
Requirements
- Omada controller v6
Configuration
Getting device information and customizing your topology
Step 1. First, enter the topology map in Omada Controller. With the latest version 6, it lies under the Dashboard > Topology, as shown below.
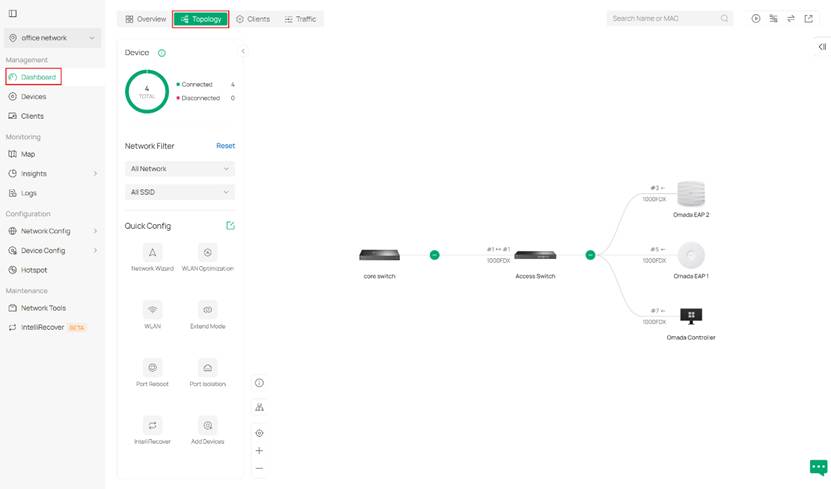
Step 2. When hovering your mouse on a specific device, you can see some of its relevant information including traffic, model type, IP address and Mac address.
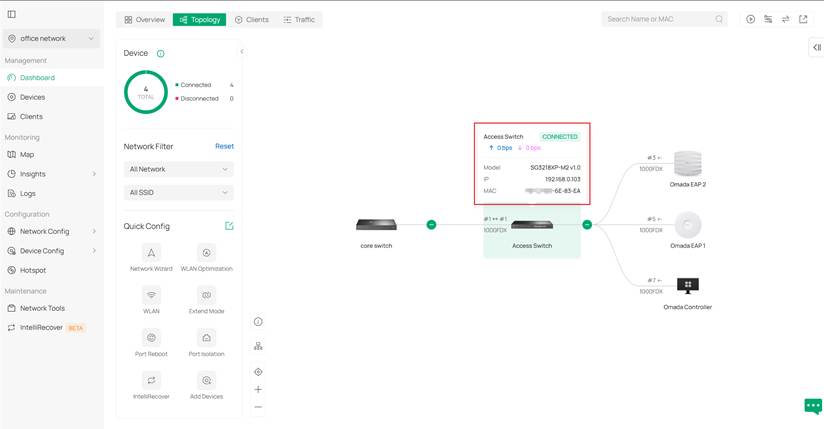
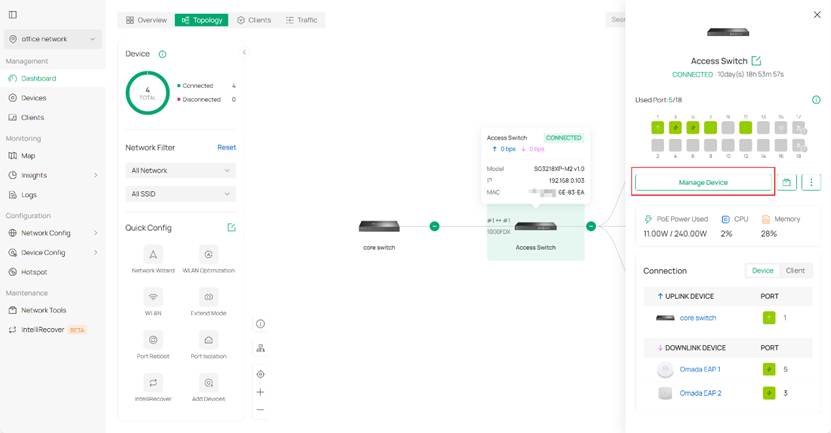
Step 3. If these are not enough for you, you may click the device to open its detailed drawer page for more information, just like in previous versions. If that still doesn't feed your need, click Manage Device to get a full page of device configuration.
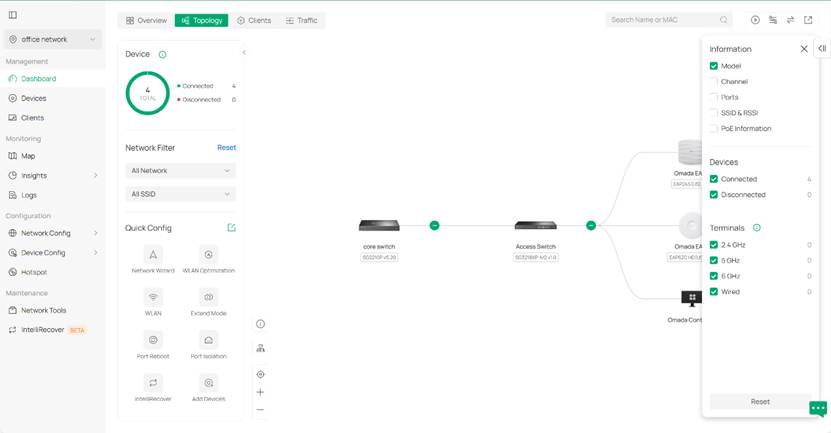
Step 4. Omada Network V6 supports to customize the information shown on the topology view by using the tools on the top right. You can show traffic, set filters and change root node of the topology by using these tools. For example, if you don’t want to see ports but instead want to see the device model on the topology view; therefore, please go to the filter on the top right, select the model option, and deselect the ports option.
Filtering and highlighting devices in the network topology
Step 1. We have a network filter for quickly reviewing and checking if the network is set as expected. It’s on the left side of the topology page.
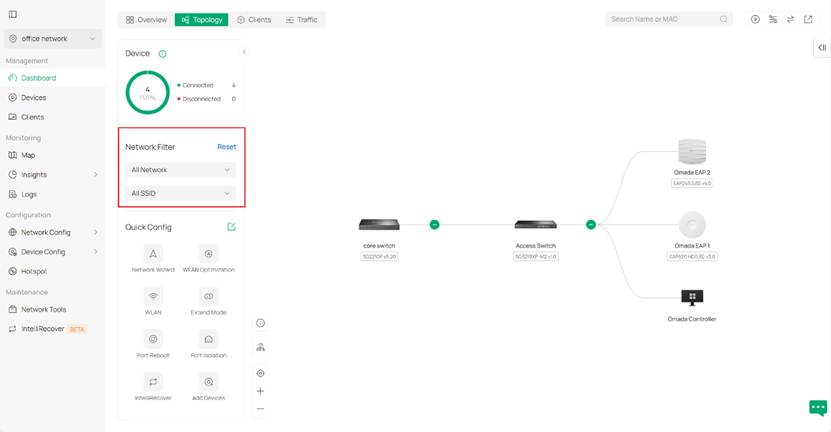
Step 2. We use the network filter to get a specific topology view about a specific VLAN. Here lies three different display to demonstrate different VLAN networks as examples.
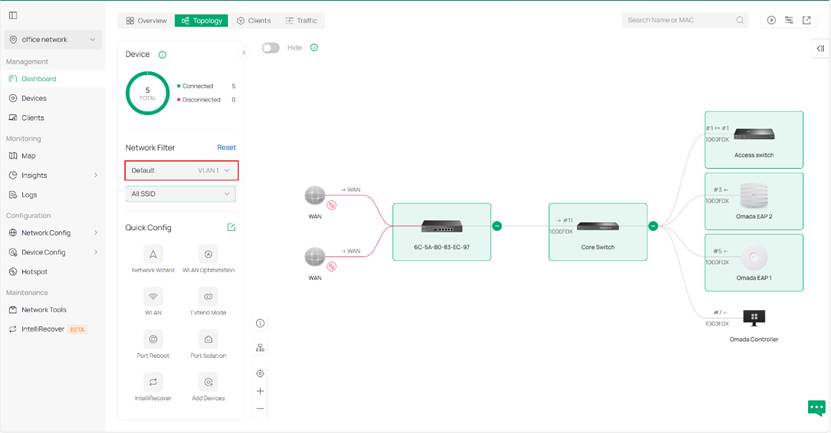
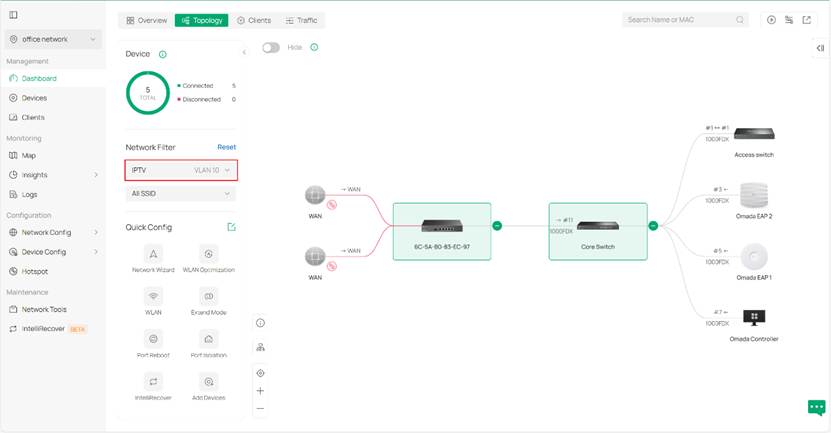
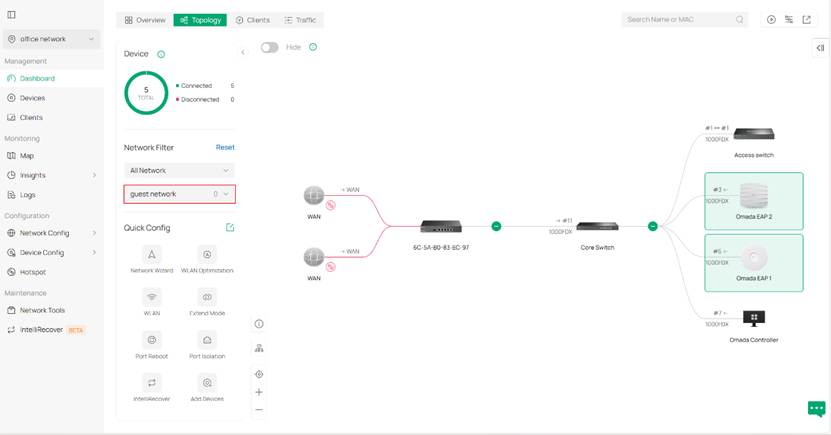
The device will be highlighted if any of the following conditions are met:
For gateways
- The gateway functions as a DHCP server.
- There exists a LAN port whose PVID matches the current VLAN.
- There exists a downstream port with status up, and the current VLAN is among the VLANs configured on that port.
- For wireless routers, the wireless component follows the highlighting rules applied to APs.
For switches
- The switch functions as a DHCP server or relay.
- There exists a port whose PVID matches the current VLAN.
- There exists a port with status up, and the current VLAN is included in its tagged or untagged VLAN list.
- The switch is configured with OUI-based VLAN.
For access points
- There exists a port whose PVID matches the current VLAN.
- There exists a port with status up, and the current VLAN is included in its tagged or untagged VLAN list.
- There is an SSID whose VLAN includes the current VLAN (SSID override VLAN configuration takes precedence). If the SSID is set to default, it is considered associated with the default VLAN.
- The encryption type is PPSK without RADIUS, and the VLAN configured in the corresponding profile’s PSK matches the current VLAN. (The number of PPSK entries is limited based on the device’s supported capacity.) If the PSK has no VLAN value, it is considered associated with the default VLAN.
For OLTs
- The S-VLAN includes the current VLAN.
An SSID is considered associated with a VLAN if any of the following conditions are met: Either the encryption type is PPSK without RADIUS, and the VLAN in the corresponding profile’s PSK matches the current VLAN, (If the PSK does not specify a VLAN, it is considered associated with the default VLAN.), or the SSID’s VLAN includes the current VLAN. (If the SSID is set to default, it is considered associated with the default VLAN.)
Conclusion
Start customizing your topology display interface from Omada Network v6!
Get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.







