What is TP-Link EAP/CAP Airtime Fairness?
Why do we need Airtime Fairness?
Traditionally, your phones, laptops, pads or any other devices need to compete for the chance to transmit and receive data when they are connected to the same Wi-Fi signal. In this situation, once a slow transmitting device gets the chance, it will take longer time to send or receive the data. In the meanwhile, other faster devices must wait until the slow device finishes the transmitting process. Based on the above situation, you might want to cut down time given to legacy devices to allow faster devices download data for longer times. This will significantly increase overall capacity of the network. To achieve such objective Airtime Fairness is introduced.
How does Airtime Fairness work?
Airtime Fairness feature is based on TDMA technology, short for Time Division Multiple Access. It divides the Wi-Fi signal into many same time slots, and each Wi-Fi device takes turns to send or receive data from the Internet within its own time slot. In this way, the capacity and efficiency of Wi-Fi will be improved.
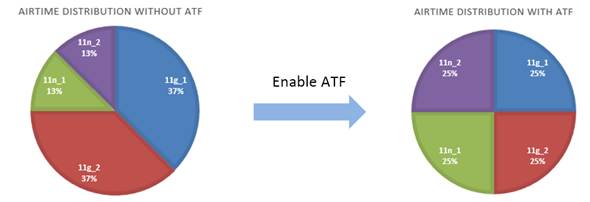
As shown above, without Airtime Fairness, those slow clients need more time to transfer the same data, which decreases Wi-Fi efficiency.
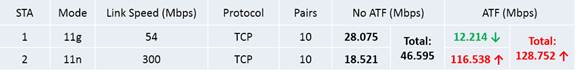
With two different speeds of clients connected to the same Wi-Fi, the test result below shows us the improvement of Airtime Fairness. When Airtime Fairness is disabled, the download speed of 802.11g client is 28.075Mbps while 802.11n client is 18.521Mbps. But when Airtime Fairness is enabled, the download speed of 802.11g client is 12.214 while 802.11n client is 116.538Mbps, which is highly improved. The overall throughput of Wi-Fi has tripled (from 46Mbps to 128Mbps).
Which TP-Link products support Airtime Fairness? How to enable this feature?
So far EAP225-Outdoor_V1, EAP320_V1&V2, EAP330_V1&V2 and CAP1200_V1 support Airtime Fairness feature. This feature can be found and enabled in Wireless Advanced settings of the products.







