Contents
IGMP Join Messages Not Sent or Dropped
IGMP Proxy or Snooping Misconfiguration
Insufficient Bandwidth or Packet Loss
Wireless Interference or High AP Load
Excessive Broadcast/Unknown Multicast Storm
Objectives
This guide helps you quickly identify and resolve IPTV network issues.
It covers end-to-end troubleshooting steps, from terminal devices to gateways, and analysis of key factors that affect IPTV performance, including multicast signaling errors, bandwidth bottlenecks, wireless interference, and broadcast storms.
Requirements
Network environment: Layer 2 or Layer 3 multicast network that supports IPTV services
Device types: TP-Link Omada Series (APs, Switches, and Gateways)
Key features: IGMP Snooping, IGMP Proxy, PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast), QoS (Quality of Service), and Storm Control
Auxiliary tools: Omada Controller, packet capture tools (e.g., Wireshark or Packet Capture), and bandwidth and latency testing tools (e.g., SpeedTest or iPerf)
Introduction
IPTV delivers video streams to multiple users through multicast technology. Abnormal IGMP messages, multicast misconfigurations, or issues like bandwidth limits, wireless interference, and multicast storms can degrade video performance, causing black screens, freezing, distortion, mosaic artifacts, or delayed channel switching. When troubleshooting IPTV issues, it is recommended to follow a sequential approach: Terminal > Wireless Access > Switching Layer > Gateway Layer.
Troubleshooting Guide
I. IGMP Join Messages Not Sent or Dropped
Typical Symptoms
Black screen during playback, channels not loading, or frequent video freezing.
Possible Causes
The terminal fails to send IGMP Membership Report messages correctly, or network devices block or fail to forward IGMP packets.
Troubleshooting Steps
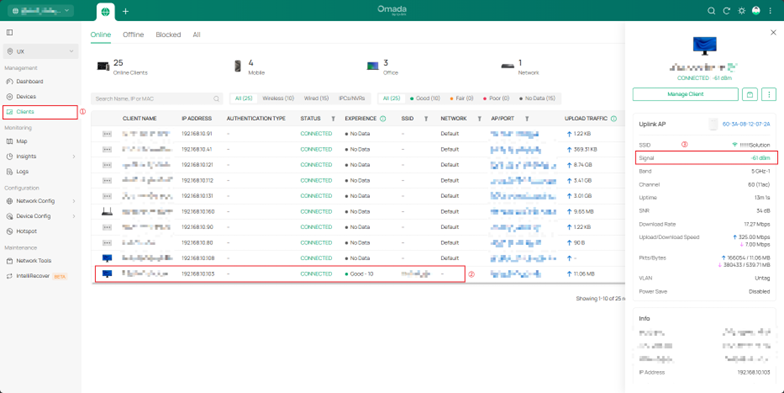
1. Terminal Layer: Use a packet capture tool to verify whether IGMP join messages are sent.
- If no IGMP join message is detected, try restarting the terminal or restoring it to its factory settings.
- Use a wired connection to reduce packet loss.
- For wireless connections, ensure the correct SSID is used and that the signal strength is -60 dBm or higher.
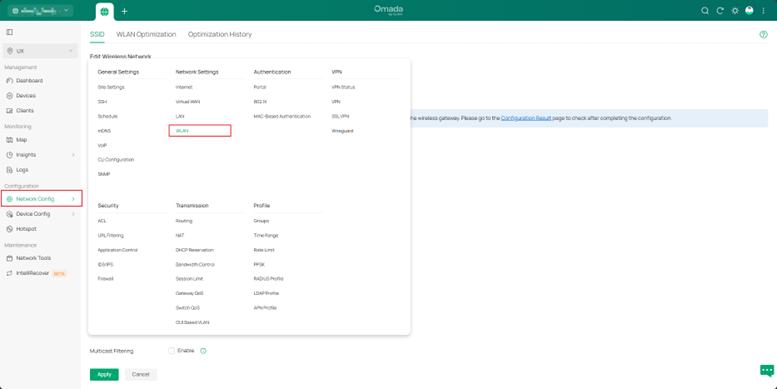
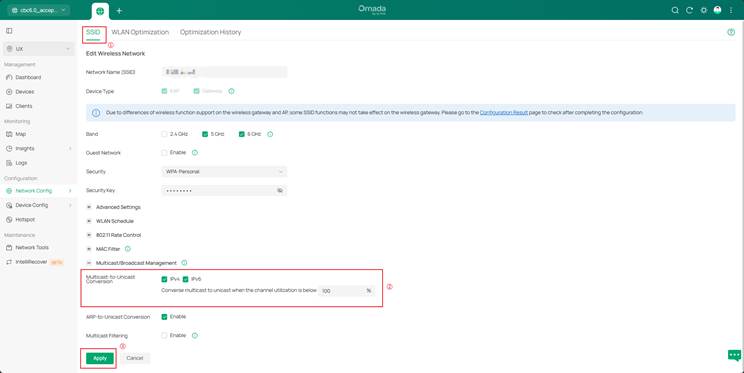
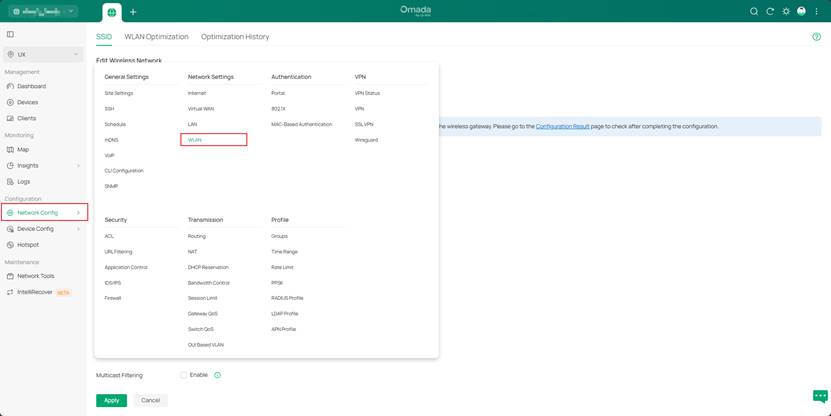
2. Wireless Access Layer (APs): In the Omada Controller, enable Multicast-to-Unicast Conversion (Site > Network Config > WLAN > [SSID] > Edit > Multicast/Broadcast Management) to improve the stability of wireless transmission. Optimize channels, prioritize the 5 GHz band, and limit low-rate clients that can slow down traffic.
3. Access Layer Switches: Enable IGMP Snooping to ensure multicast tables are correctly updated.
- Fast Leave: Enable for single-layer networks; disable for multi-tier cascading networks.
- Query Interval: Set IGMP to 125 seconds, IGMP Snooping to 60 seconds, and Membership Timeout to 260 seconds.
- Verify that the uplink port allows IPTV VLAN passthrough.
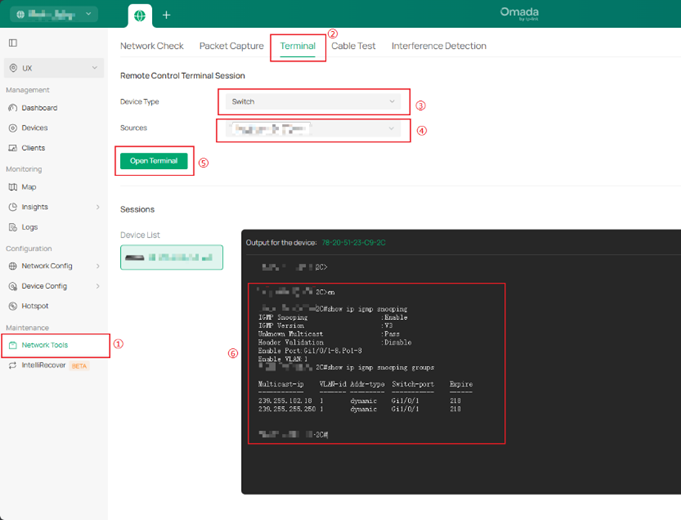
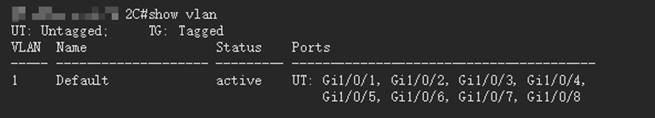
4. Aggregation/Core Switch: Verify that each VLAN has only one Querier.
- Querier Interval: Set IGMP to 125 seconds, IGMP Snooping to 60 seconds, and Membership Timeout to 260 seconds or higher.
- Enable PIM or IGMP Proxy to ensure multicast packets are properly forwarded.
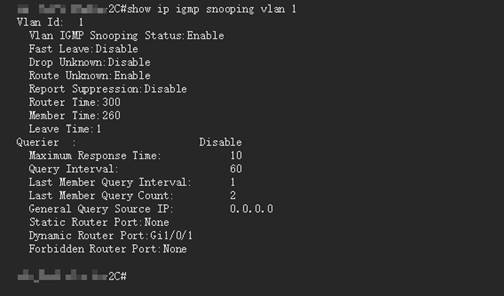
5. Gateway Layer:
- Verify that IGMP Proxy or PIM is properly enabled.
- Ensure the WAN port is correctly bound.
- Confirm that VLAN mapping is properly configured in multi-VLAN networks.
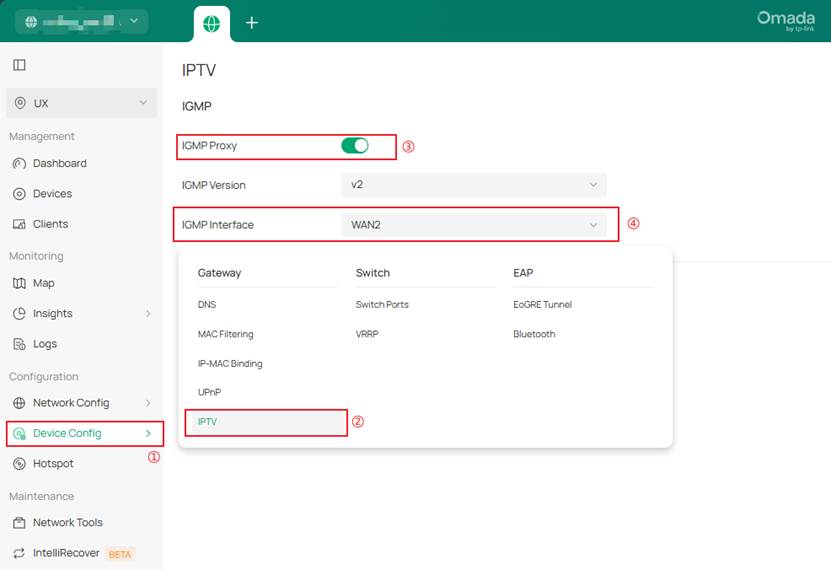
II. IGMP Proxy or Snooping Misconfiguration
Typical Symptoms
The terminal can connect to the network but fails to play video or experiences unstable streams.
Possible Causes
Inconsistent IGMP configurations across devices cause multicast table desynchronization.
Troubleshooting Steps
1) Ensure that IGMP functionality is enabled on all devices.
2) Enable Proxy on upper-layer devices and disable Querier on lower-layer devices.
3) Confirm that VLAN mapping is correct and ACLs are not blocking multicast packets.
Recommended Configuration
1) IGMP Snooping: Enabled
2) Querier: Enabled on the core switch
3) Proxy: Enabled on the gateway
III. Insufficient Bandwidth or Packet Loss
Typical Symptoms
Video stuttering, audio-video desynchronization, or noticeable latency.
Possible Causes
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) transmission does not implement retransmission mechanisms; link jitter and packet loss directly affect video quality.
1. Terminal: Use latency testing tools on the terminal side to help evaluate network quality.
- Use SpeedTest or iPerf to test link throughput.
- Check if port utilization exceeds 80%.
- Capture packets to analyze UDP packet loss and latency.
2. Access Switch: Check port bandwidth utilization and error frames. The recommended rate is at least 1 Gbps. Enable QoS and set DSCP to 46 (EF).
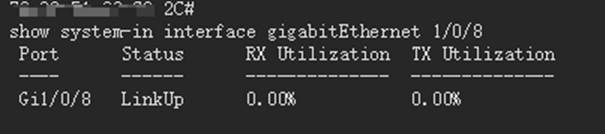
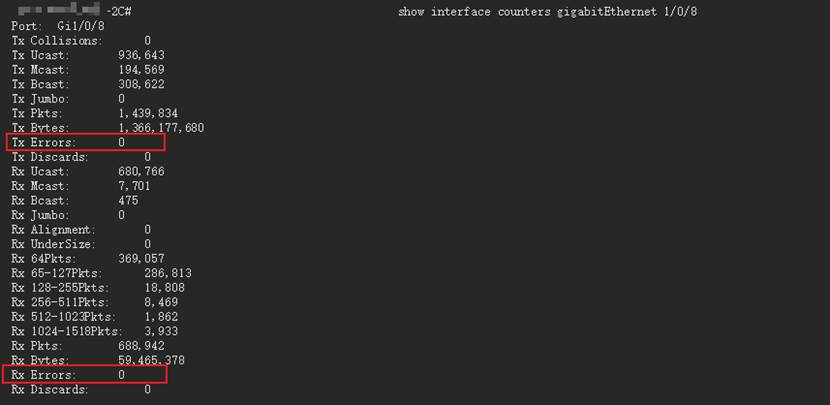
Aggregation/Core Switch: If the uplink utilization is high, enable LAG/LACP to increase bandwidth. Monitor port rate and jitter and upgrade links if necessary. Methods for checking bandwidth utilization are the same as the previous section. For switch LAG/LACP configuration, refer to the FAQ: How to configure LAG (LACP) on Omada Switches via Omada Controller | TP-Link
3. Gateway: Configure bandwidth guarantees for the IPTV VLAN. Use QoS or intelligent queue management to prioritize upstream and downstream traffic.
IV. Wireless Interference or High AP Load
Typical Symptoms
Unstable Wi-Fi playback or distorted images.
Possible Causes
Channel interference, high AP load, or insufficient backhaul bandwidth.
1. AP: Ensure each AP serves no more than 30 active clients and throughput does not exceed 200 Mbps. Use the less congested 5 GHz band whenever possible. Disable low-rate clients and perform other optimizations as needed.
2. Switch: Verify that uplink bandwidth meets IPTV concurrency requirements.
V. Excessive Broadcast/Unknown Multicast Storm
Typical Symptoms
The network slows down, IPTV playback becomes intermittent, or abnormal display issues occur.
Possible Causes
A large number of broadcast or unknown multicast packets on the network consume bandwidth and switch CPU resources. Excessive redundant packets such as mDNS or ARP may impact IPTV terminals or multicast sources, resulting in stuttering playback or image distortion on IPTVs.
1. AP: If packet capture (e.g., Wireshark) shows a large number of redundant multicast or broadcast packets on the network, configure Multicast Filtering as needed. Go to Site > Network Config > WLAN > [SSID] > Edit > Multicast/Broadcast Management, check Multicast Filtering, and select Filtering Protocols according to the packet capture results to filter unnecessary traffic.
2. Access Layer Switch: Enable Storm Control and limit the broadcast/multicast rate (recommended threshold: 2–5% of port bandwidth). For detailed configuration, refer to How to configure Storm Control on Omada Switches via Omada Controller | TP-Link
3. Aggregation/Core Switch: Ensure there is only one Querier and disable duplicate Queriers on lower layers. If excessive ARP packets are detected, apply ARP protection, ACLs, or even PIM Layer 3 isolation on wired segments to protect IPTV terminals and multicast sources from the impact of excessive traffic.
4. Gateway: Disable PIM on non-IPTV interfaces to prevent redundant forwarding.
Conclusion
With a layered approach to troubleshoot IGMP messages, multicast configuration, link bandwidth, wireless performance, and storm control, IPTV issues such as black screens, freezing, image distortion, and mosaic artifacts can be identified and resolved.
By following the configuration and parameter recommendations for TP-Link Omada devices, you can quickly restore video quality.








