Introduction
This article explains the PoE Out port priority logic and power protection mechanism for devices equipped with dual PoE Out ports that can automatically manage PoE output level.
For such devices, one is a high-priority port by default. The system would prioritize the power supply of this port during PoE negotiation and overload.
This FAQ mainly describes the default port-priority design and protection behavior under different power-supply conditions, using the EAP775-Wall as an example.
Requirements
- EAP that supports dual PoE out ports.
Configuration
Once PoE out is enabled on both ports, the following rule would take effect by default.
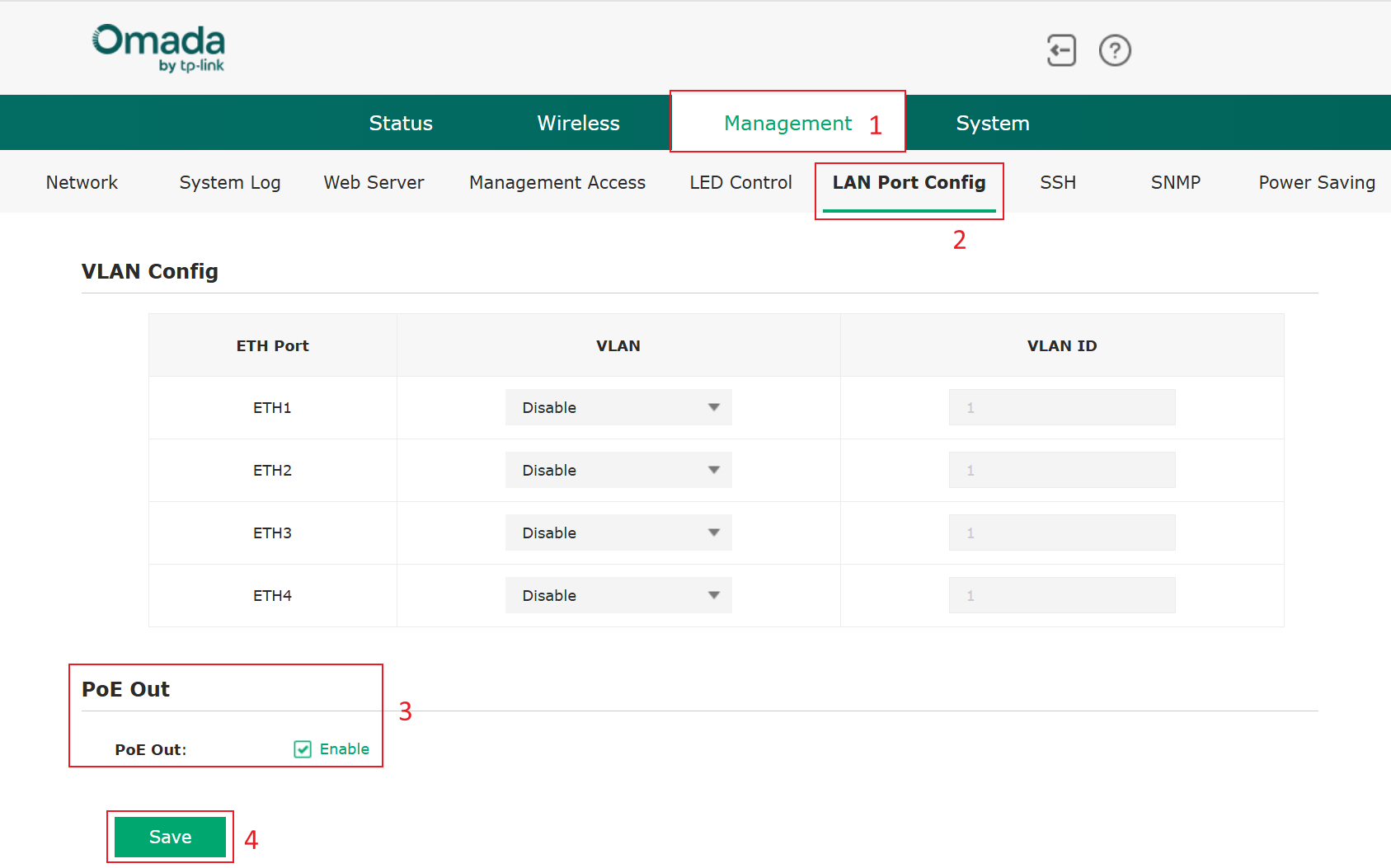
Standalone mode: Management->LAN PORT CONFIG->PoE Out, enable it, and Save
It would enable PoE on both ports.
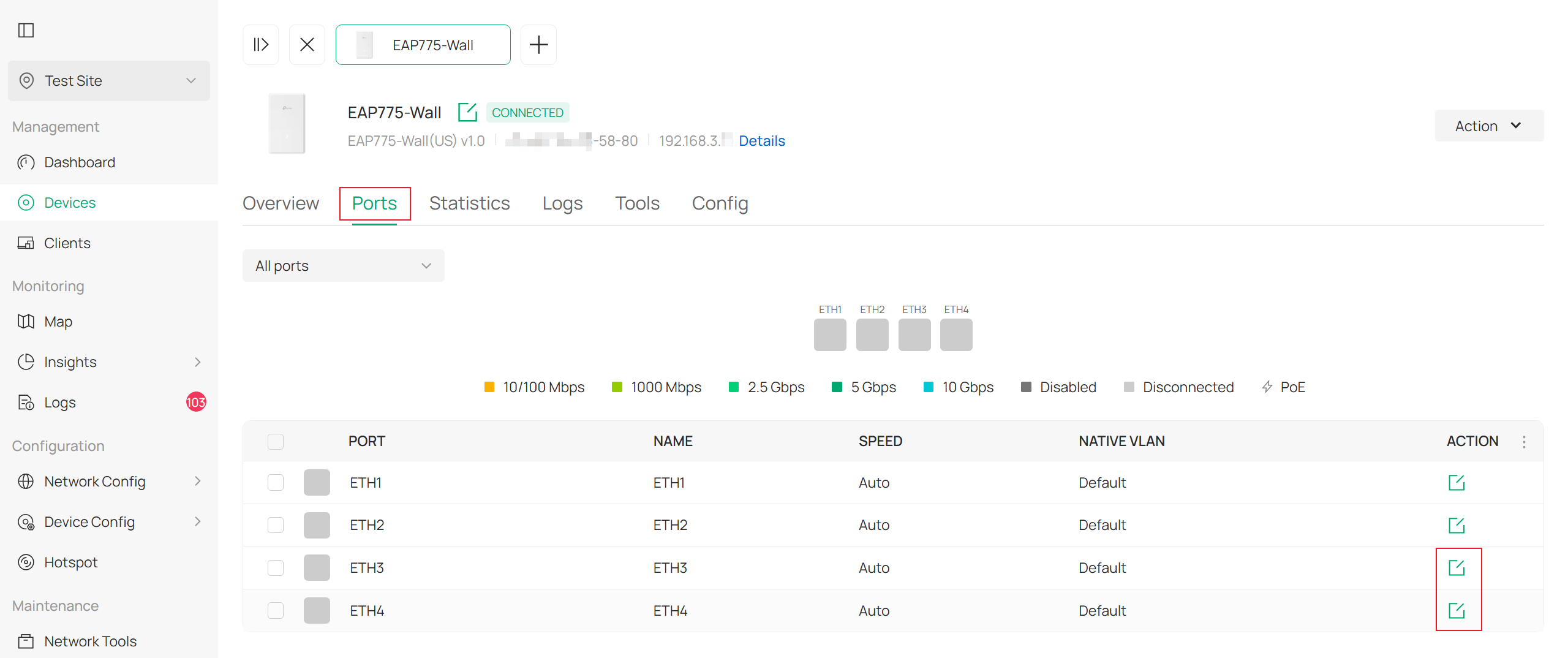
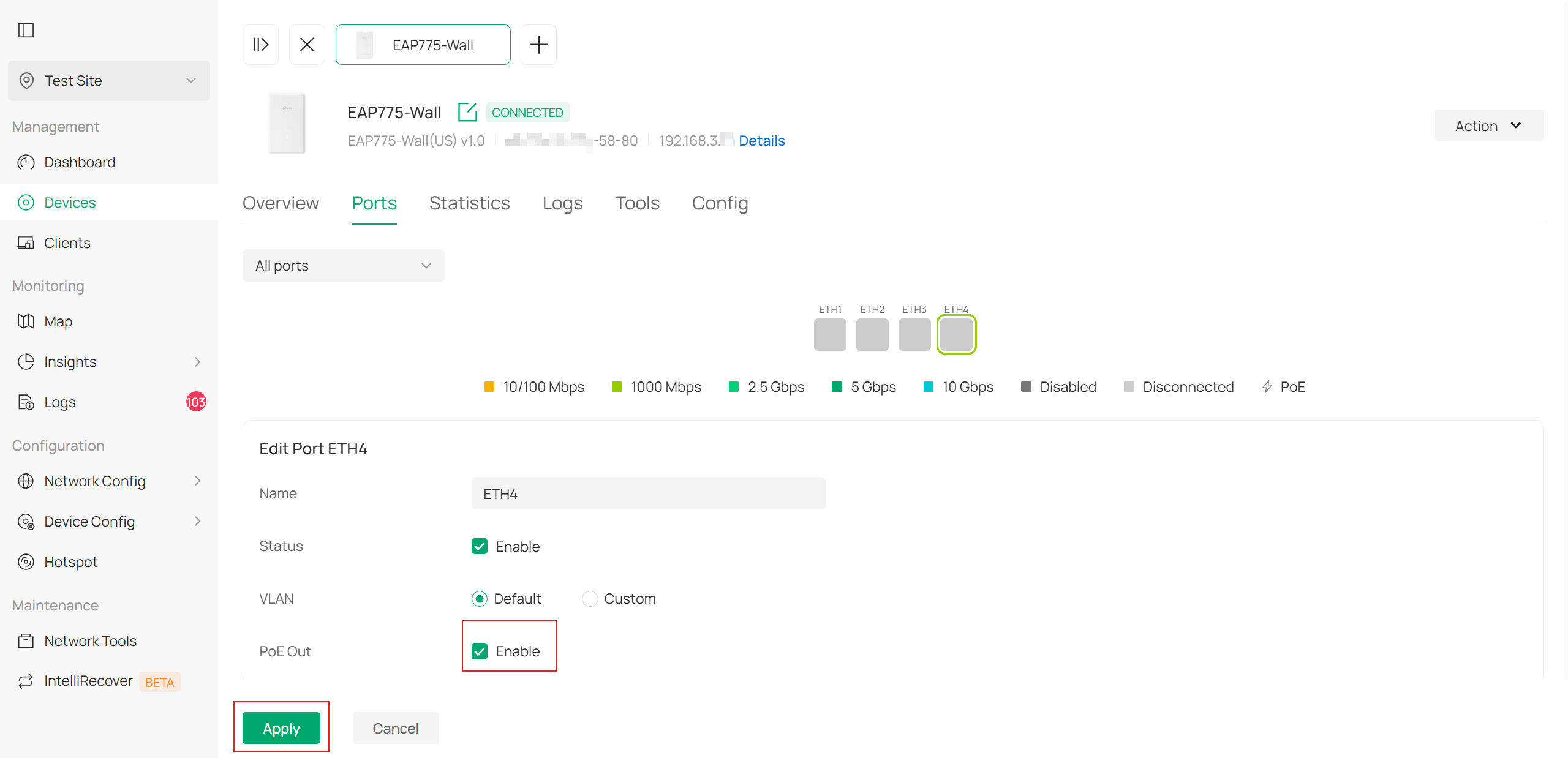
Controller Mode: Manage Device->Ports->Action->Poe Out
Here in controller mode, you could configure PoE on each port separately.
Port PoE Priority Logic
For EAP775-Wall, ETH4 is the high-priority port, and ETH3 is the low-priority port. It supports one PoE+(802.3AT) out port or two PoE(802.3AF) ports, with ETH4 being the High-Priority Port.
The detailed PoE Out behavior under all possible conditions is as follows:
1.ETH4 (High-Priority Port) Negotiates IEEE 802.3AT
ETH4 supplies IEEE 802.3AT power normally.
ETH3 (low-priority port) disables its PoE Out function and does not supply power.
2.ETH4 (High-Priority Port) Negotiates IEEE 802.3AF
ETH4 supplies IEEE 802.3AF power normally.
ETH3 (low-priority port) enables its PoE Out function, performs standard PoE negotiation, and supplies power (802.3AT or 802.3AF) based on the negotiation result.
3. ETH4 (High-Priority Port) Has No Connected PoE Device
ETH4 does not supply power.
ETH3 enables its PoE Out function, performs standard classification negotiation, and supplies power (802.3AT or 802.3AF) based on the result.
Overload Protection Mechanism
To ensure the safety of both the EAP and the connected PoE devices when a power overload occurs under various conditions, the device implements the following protection mechanisms:
1. Per-Port Overload Protection:
Each port would set its own power overload threshold based on PoE negotiation result.
If overload is detected on one port, the PoE function on this port would be disabled.
2.System Power Overload Protection
If no individual port overload occurs but the total system power exceeds the limit, the device will first disable the PoE Out function of ETH3 (low-priority port).
If the total power remains overloaded after disabling ETH3, the device will then disable the PoE Out function of ETH4 (high-priority port) to stop power output.
Get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.








